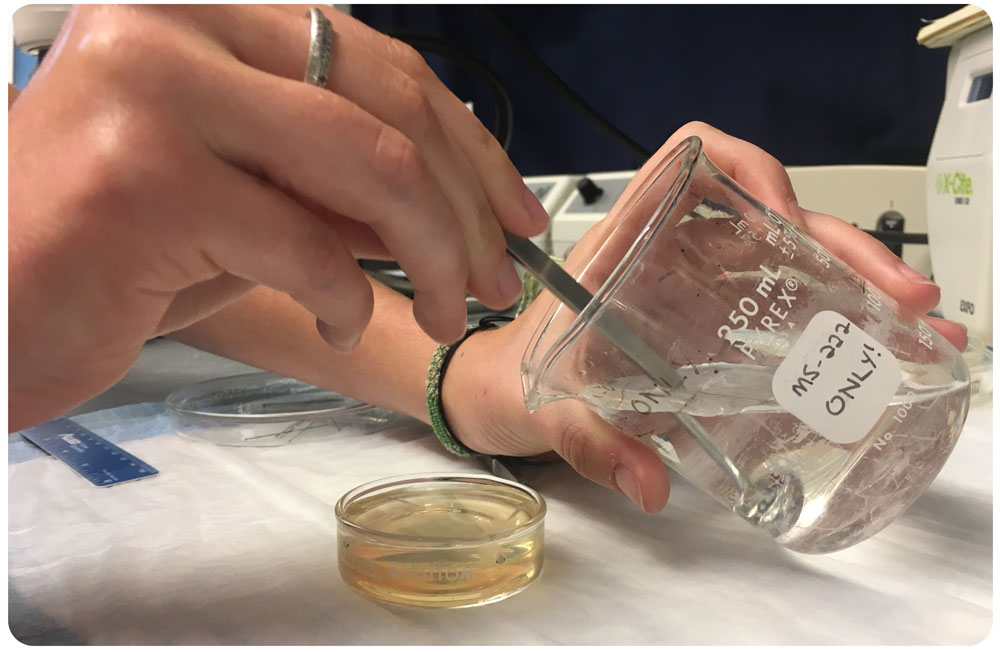
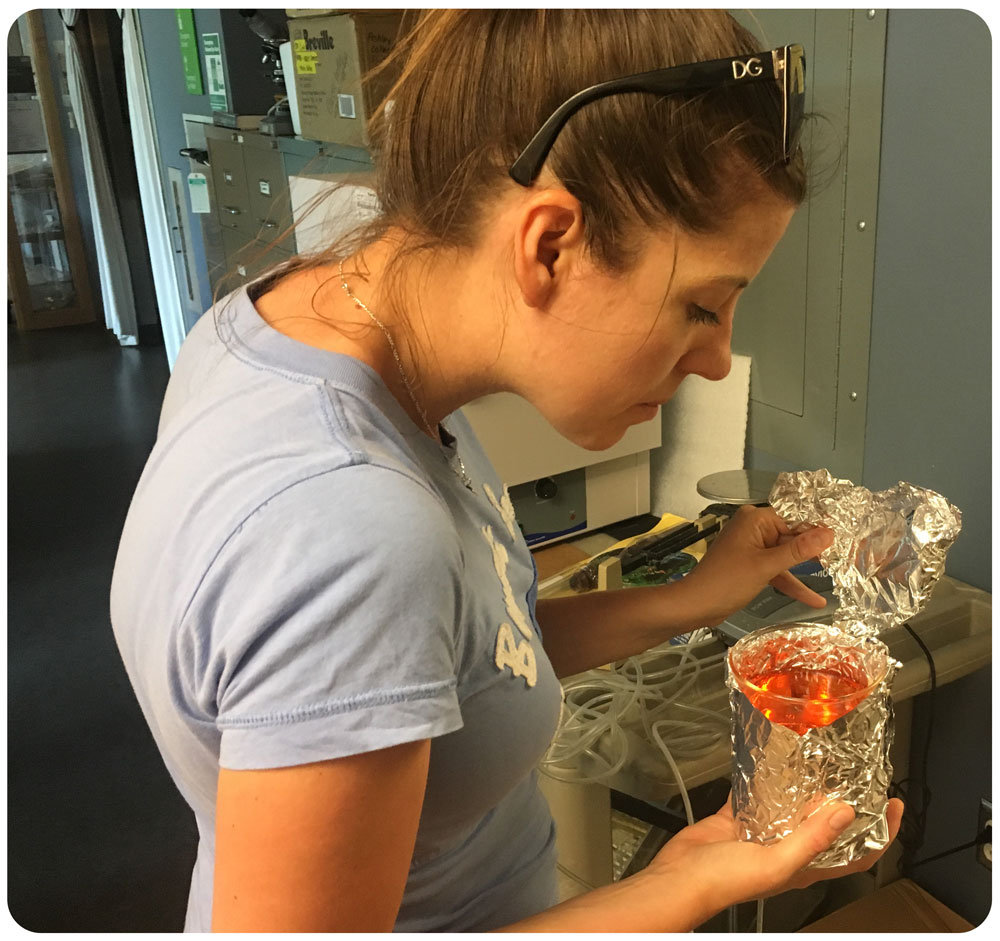
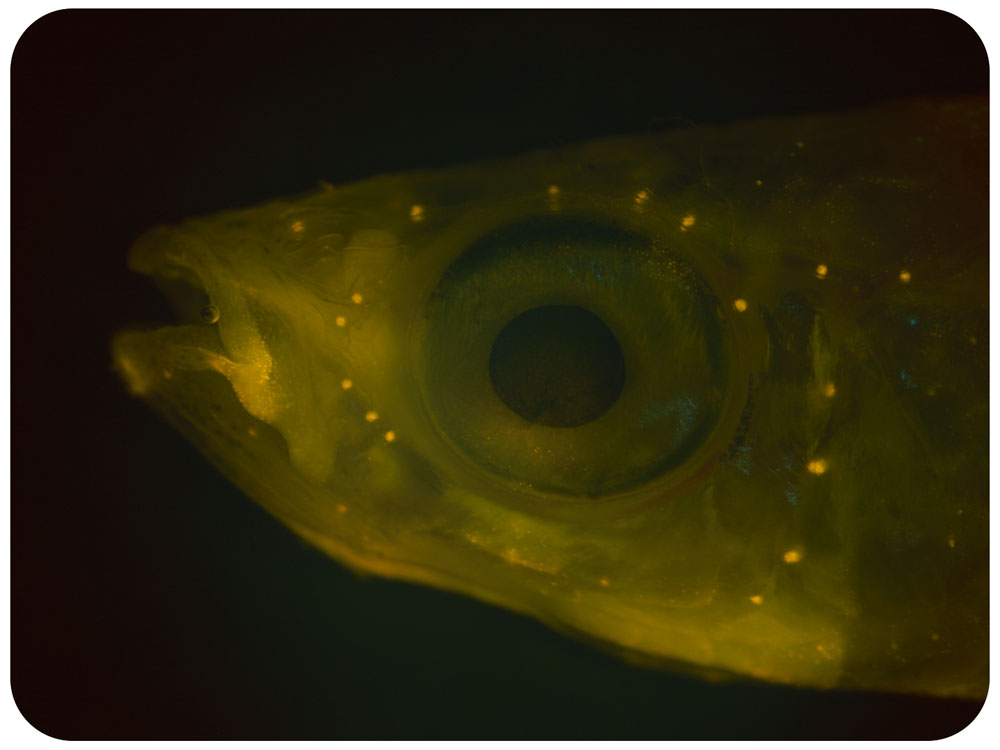
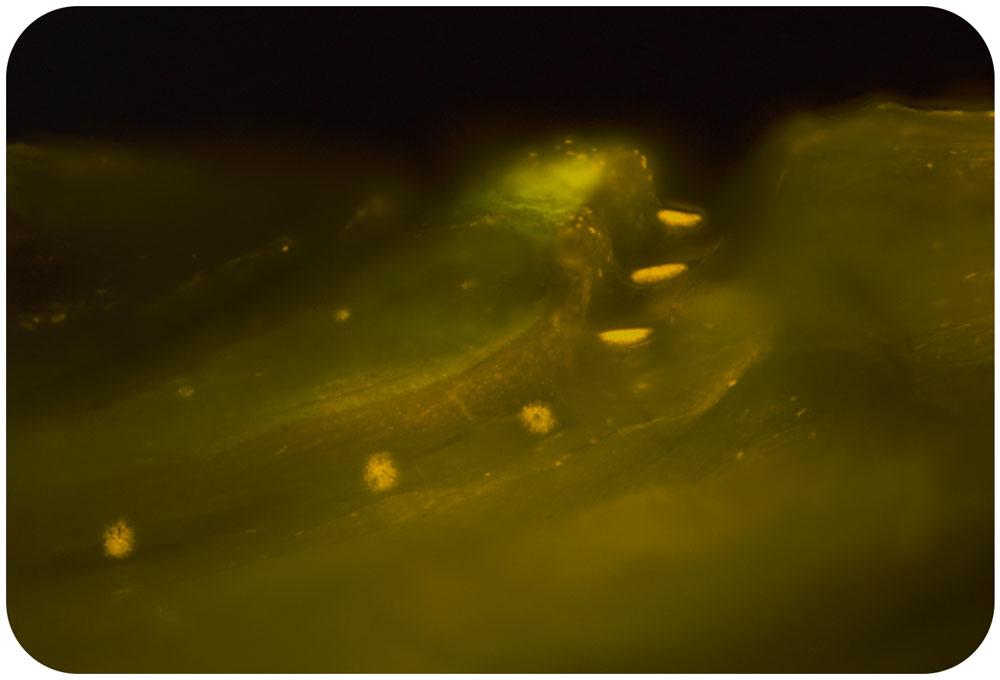
This technique involves placing live fish in a fluorescent mitrochondrial stain for 5 minutes before imaging different areas of the fish under a dissecting microscope equipped with an epiflourescence light source. This allowed us to visualize small sense organs called neuromasts located in tubular canals in the head, trunk and tail, which form the fish sensory lateral line system used to detect water flows.