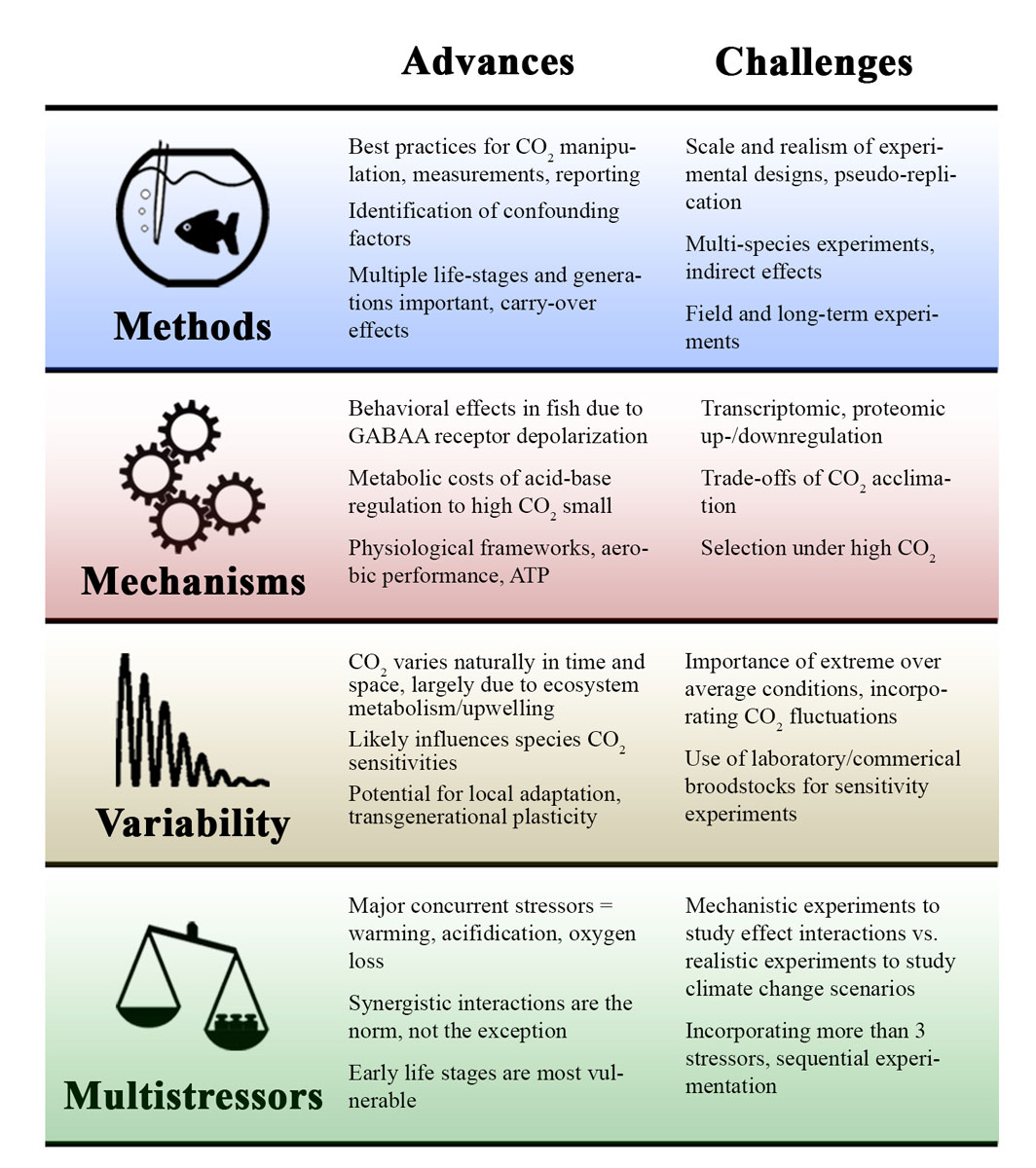
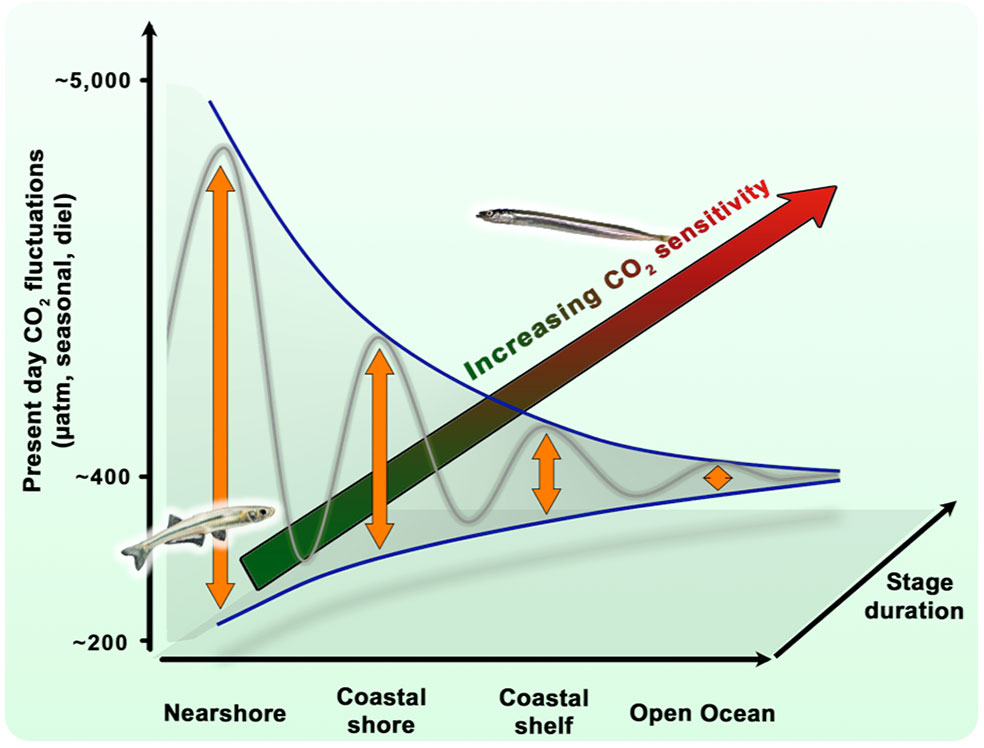
By Emma Siegfried.
Austevoll, 10 February 2026. More than two months into my research stay here in Norway, things are going pretty well. Instead of one single experiment, we actually ended up running 3 separate experiments at once because the female fish took their sweet time to get ready to spawn.
As I learned, it is quite common in the tanks here that only a few females become ready to spawn at a time, which meant that a new trial had to be started again and again.
Our first spawn was now exactly 4 weeks ago, and I'm happy to report that our first embryos in the 10˚C treatment started hatching last week! Now we’re counting the larvae that are hatching each day, taking photos of them on the day of hatch and then also taking videos of their hearts to measure heart rate.
The hatchlings are then preserved, mostly in ethanol but also in RNAlater for potential further genomic and transcriptomic analyses.
I have now only a month left here in Norway, and I’m excited that the experiment is going well. At the same time, I’m ready for it to be over so that I can start analyzing data and seeing what results we have found!