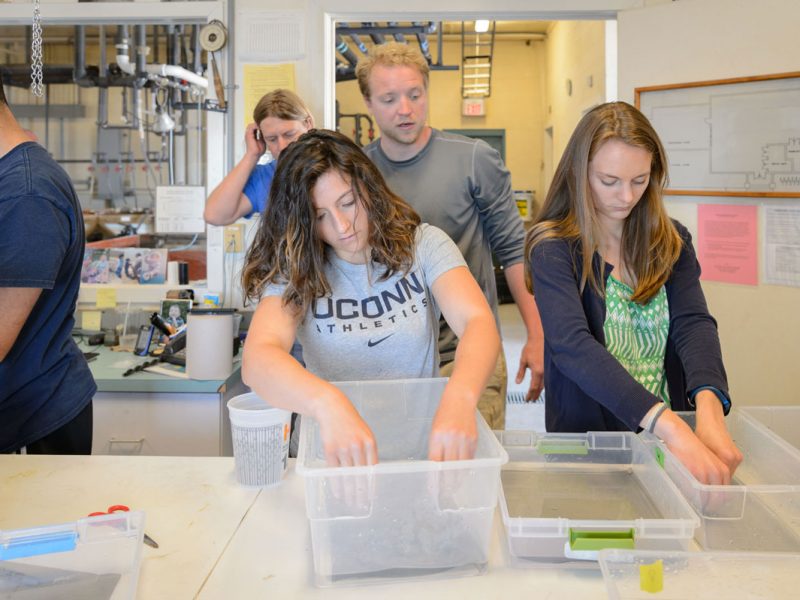
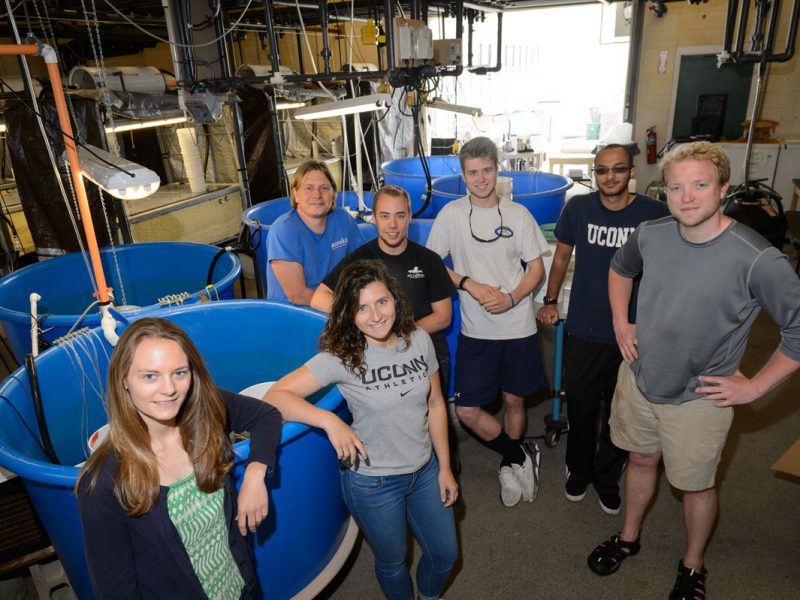
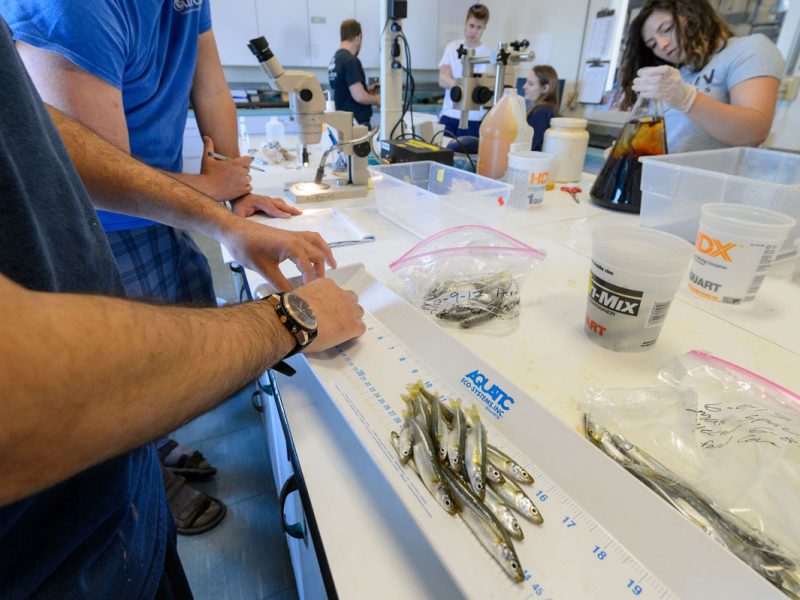
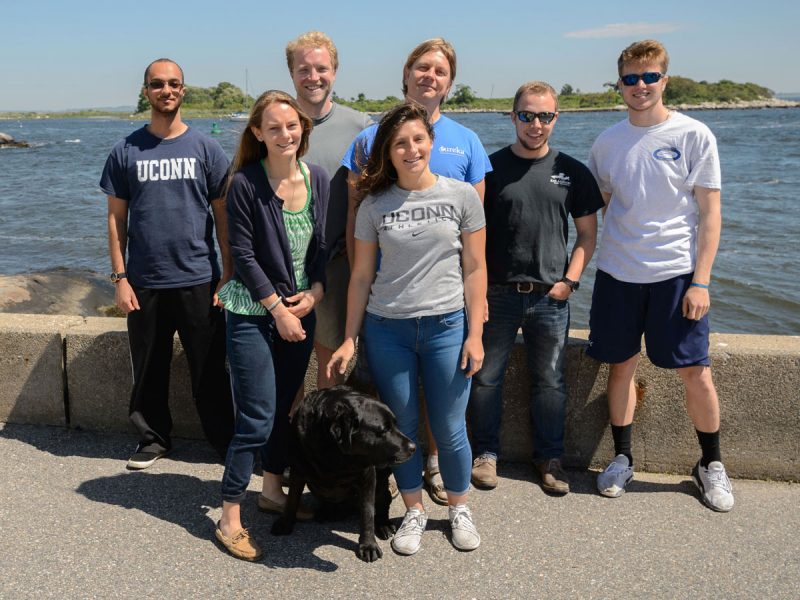
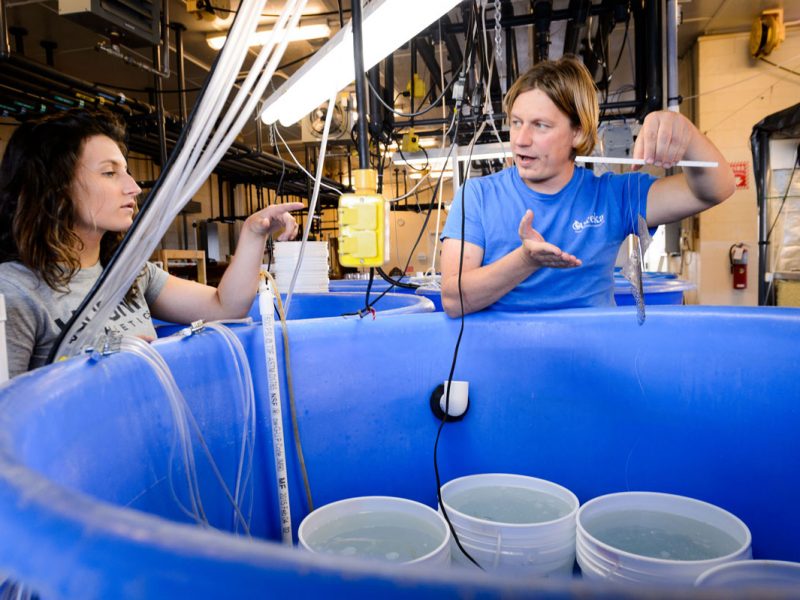
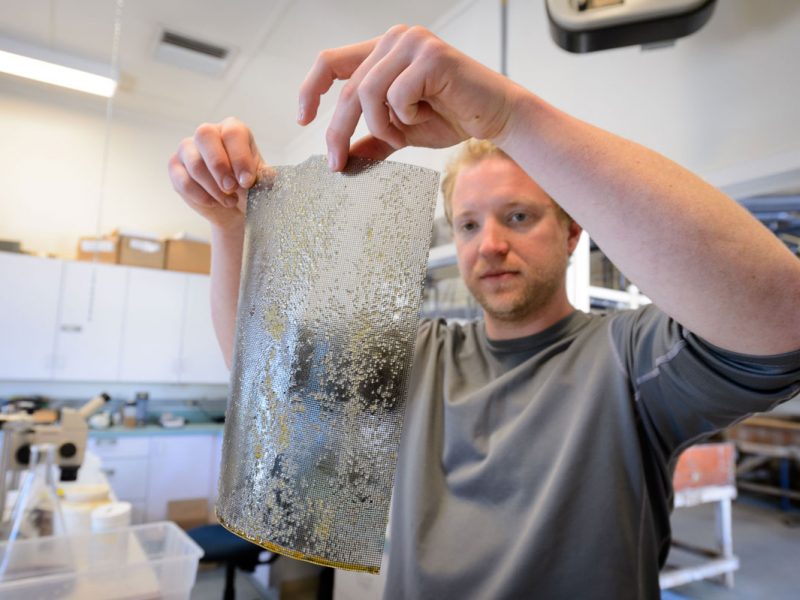
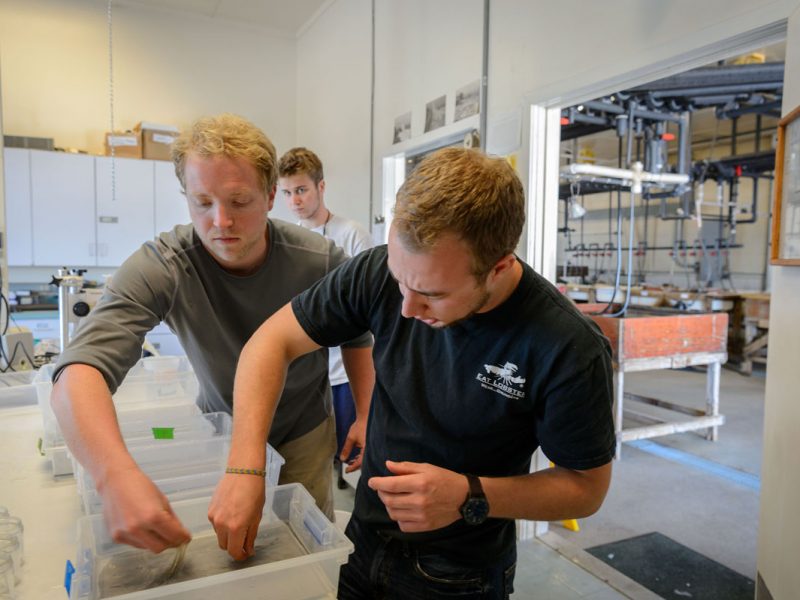
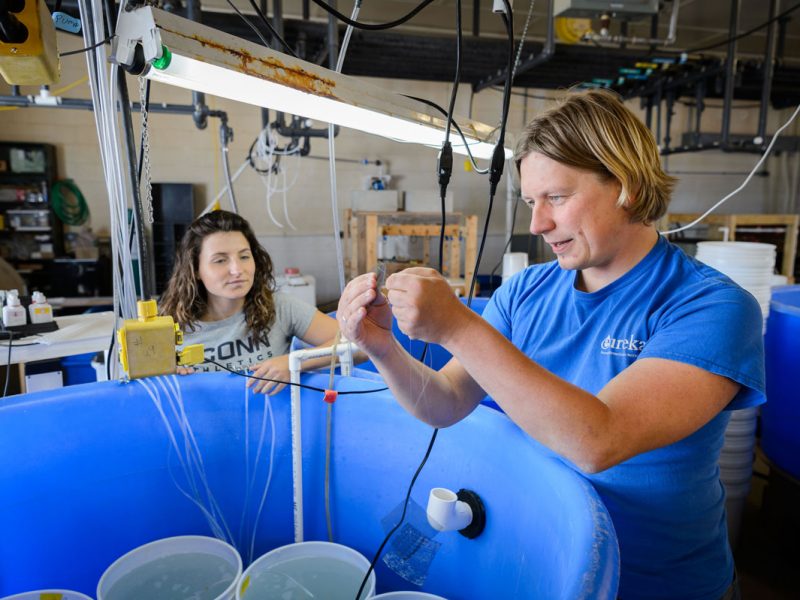
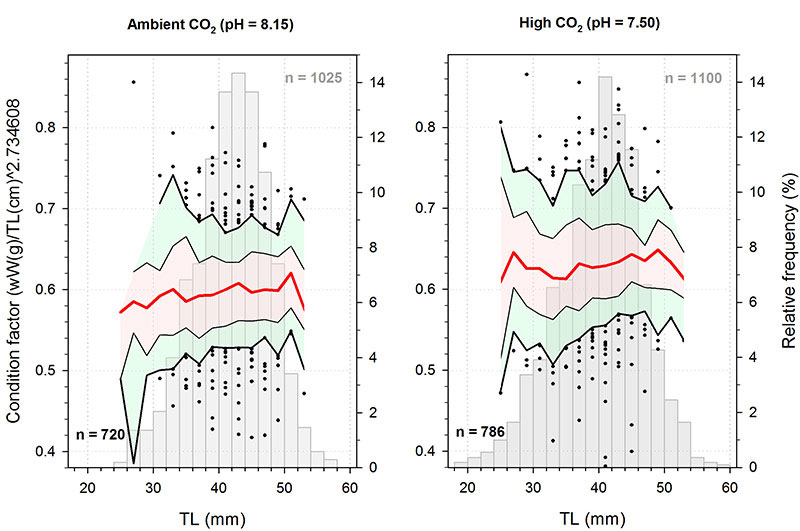
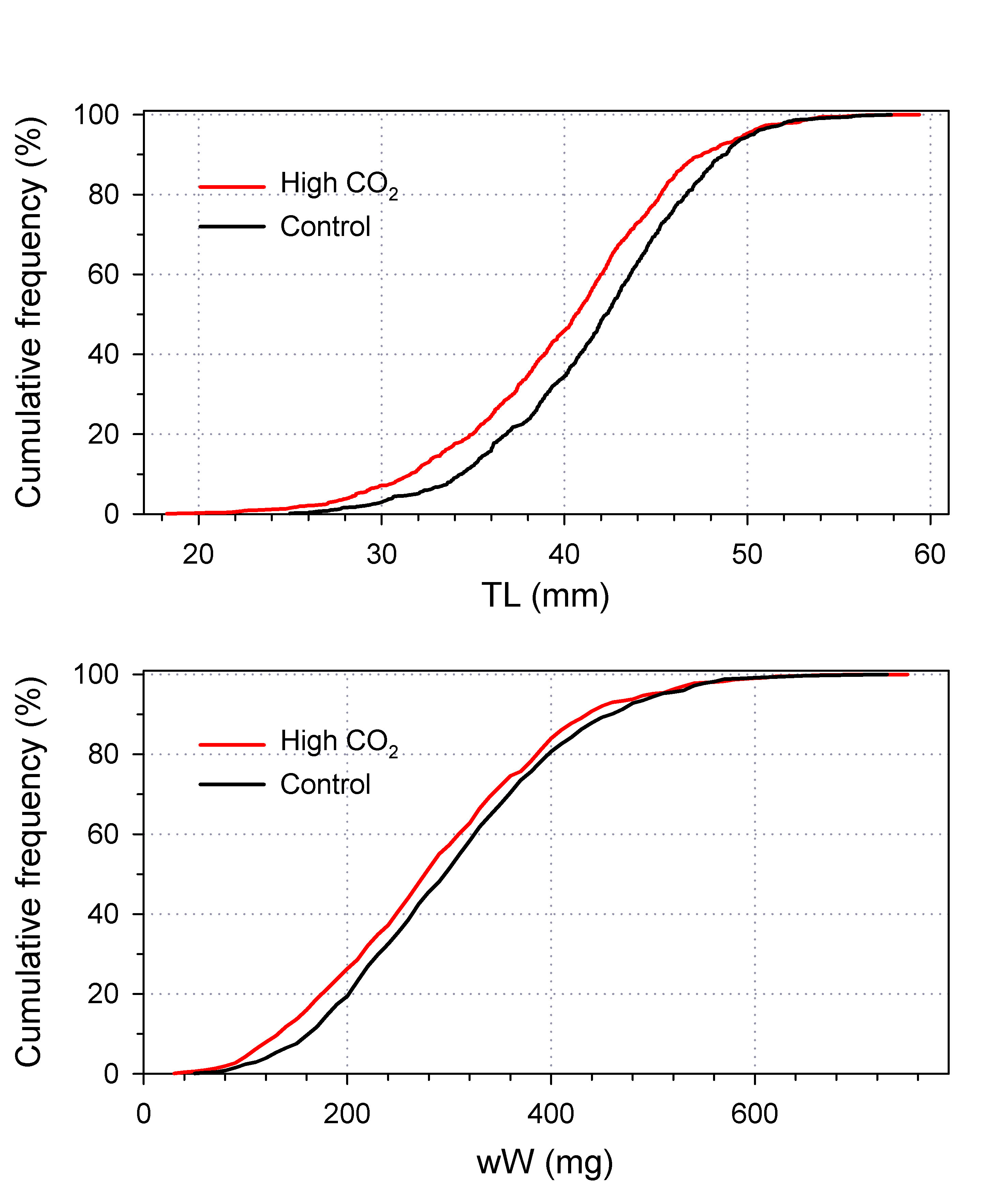
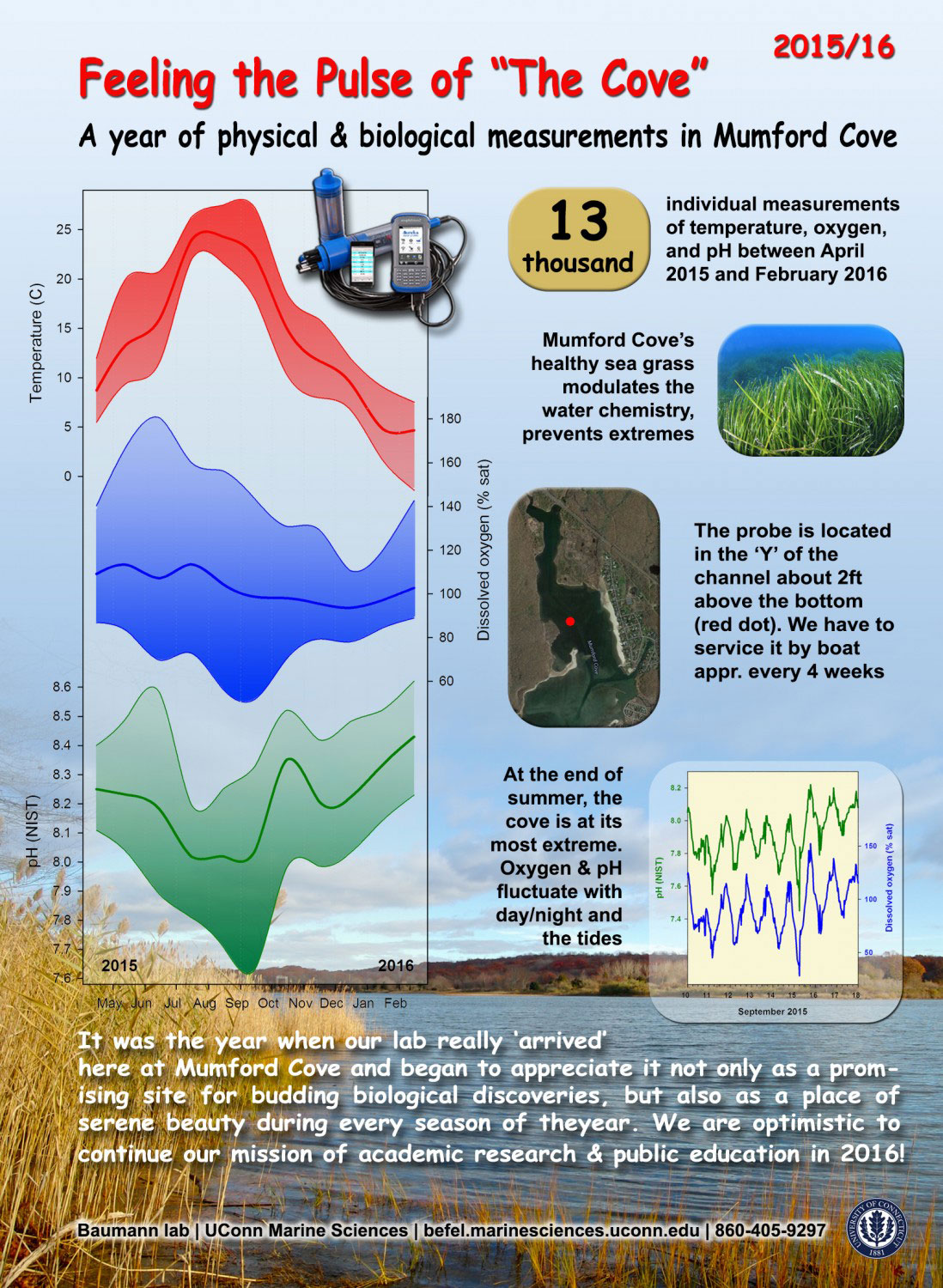
It’s the beginning of June, and in the Baumann lab that means: high time for experimental research on the Atlantic Silverside, the famous forage fish and important model species! This year, we have several major objectives; our NSF-sponsored research examines the sensitivity of offspring to the individual and combined effects of high CO2 and low oxygen (Chris Murray), while in collaboration with our colleagues from Cornell University we rear several families for genetic and transcriptomic studies. Elle Parks, our REU student just started her work on the effects of CO2 and temperature on the starvation resistance of silverside larvae. As always, the days when new experiments start are a group effort, where everybody including many volunteers help. Thanks to Peter Morenus (UConn) for the coming down for documenting the activities!
This story is also featured on UConn Today.