By H.B.
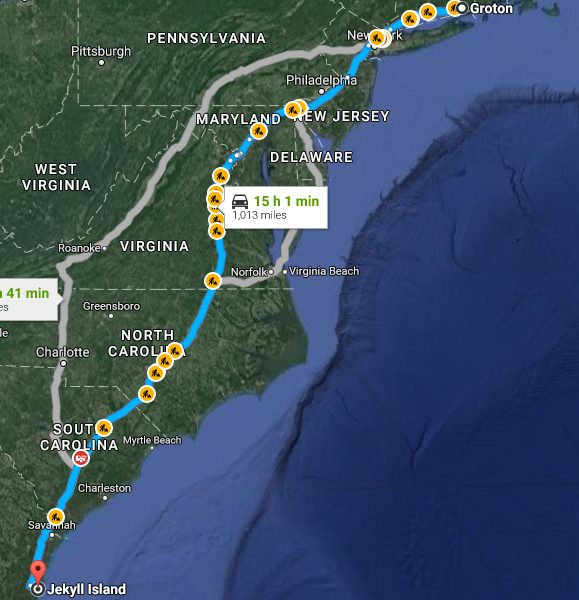
Somewhere after Richmond, VA, the sun sets and traffic on the I-95 begins moving better. At long last. The four people in the burgundy Dogde Challenger have all already cycled through their driving shifts once and dare an impatient glance at the time left. Still more than 8 hours. More than 8 hours to reach this very special location at the Atlantic coast – Jekyll Island, Georgia. In the trunk of the car a jumble of coolers and a beach seine, buckets, air pumps, and hoses topped with the crumpled witnesses of roadside dining. This is no ordinary road trip.
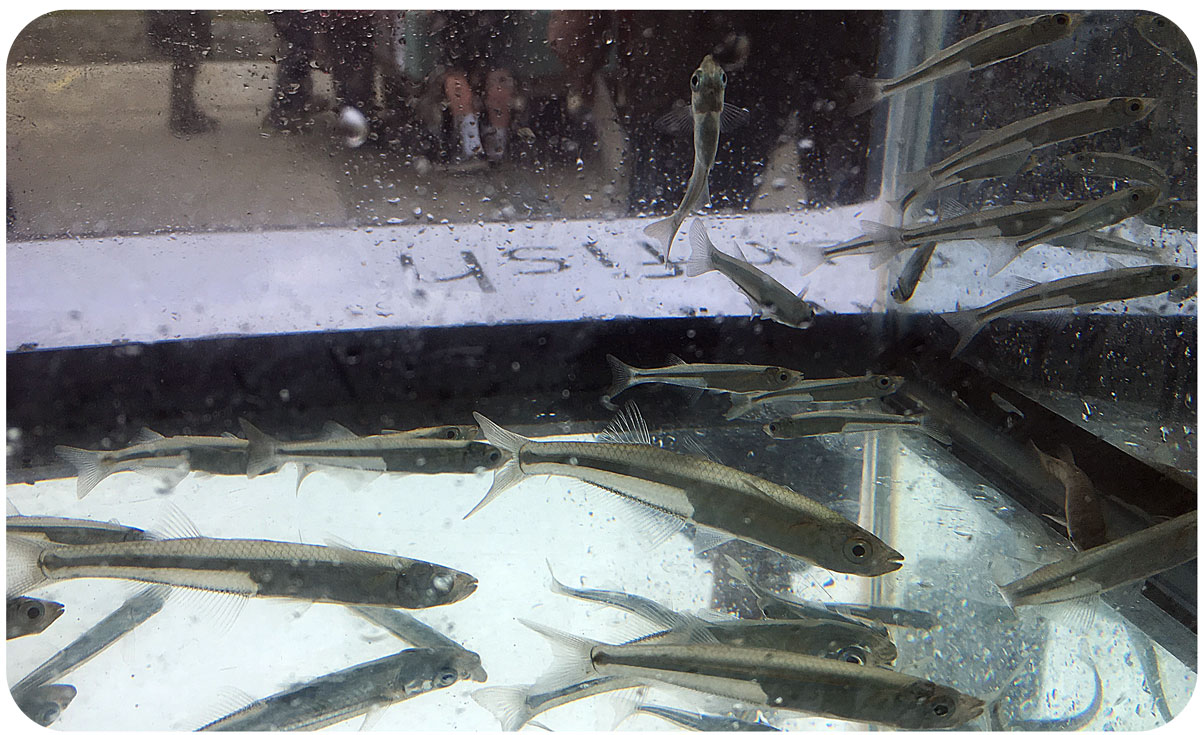
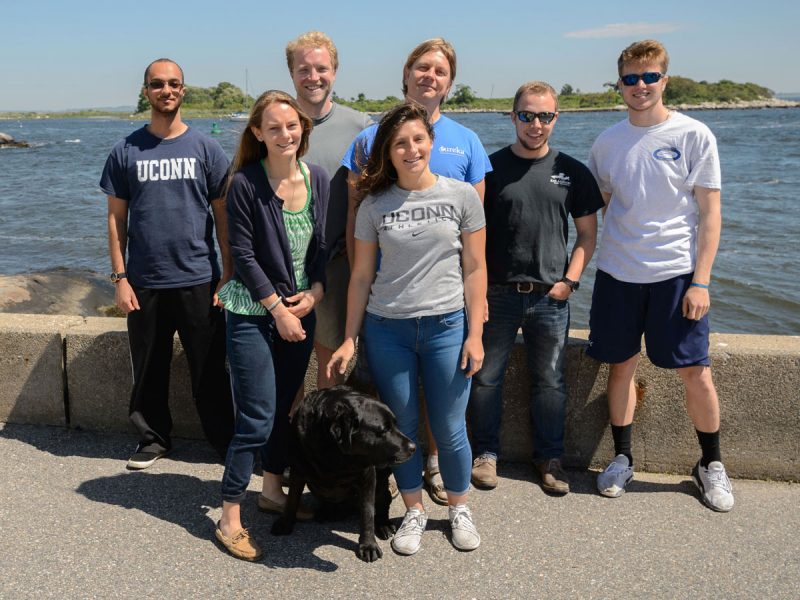
We, that are Aryn and Nicholas from the Therkildsen lab of Conservation Genetics lab at Cornell University and James and Hannes from the Fish Ecology Lab here at UConn; we went on this road trip to catch live, spawning ripe Atlantic silversides from the southern edge of the species distribution. We then intended to bring these fish back to UConn alive, sample another population from the south shore of Long Island (Patchogue, NY) and produce genetic crosses of these populations.
The broad goal of our expanding collaborative efforts with our geneticist friends from Cornell is the creation of an annotated genome of this species, which will be an important milestone in deepening or understanding of the molecular and genetic responses of organisms to local selection regimes and marine climate change. Given the Atlantic silverside’s ecological importance as an abundant forage fish along the American east coast and it’s rich history as a model organism in evolutionary and ecological studies, the annotated genome is the next logical step.
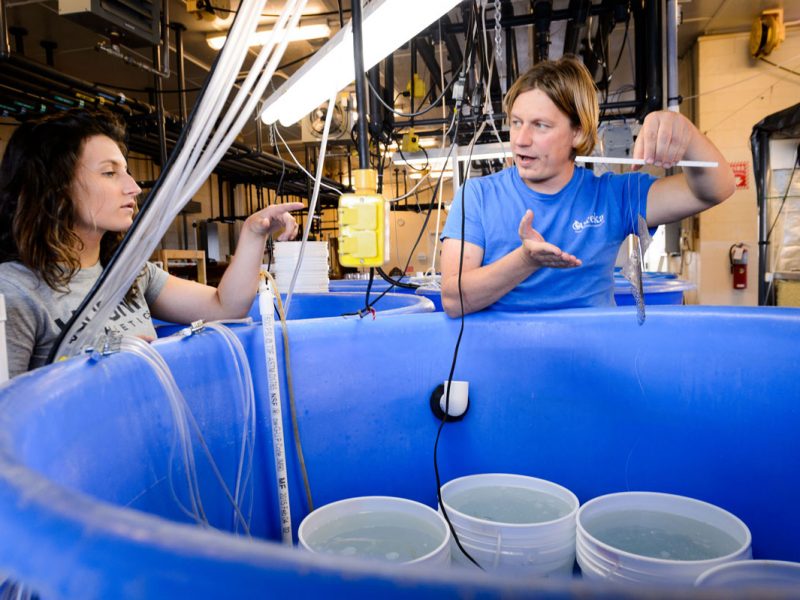
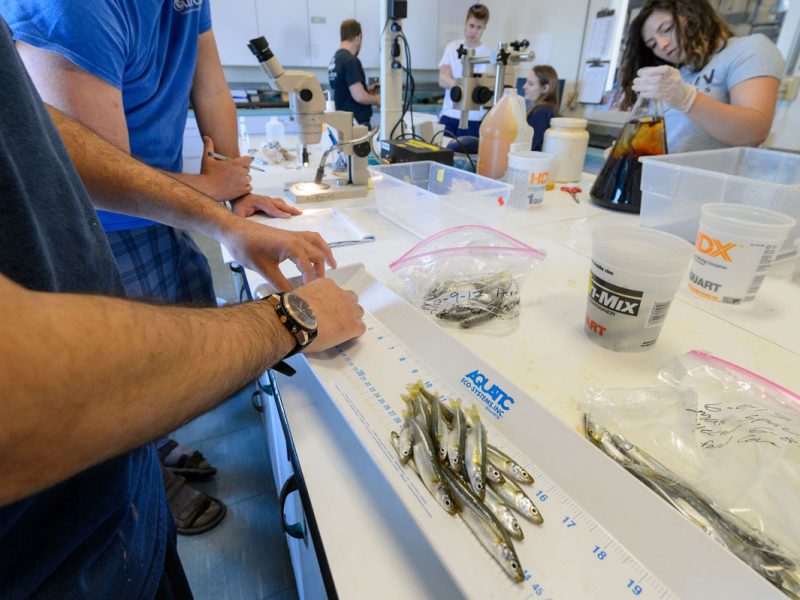
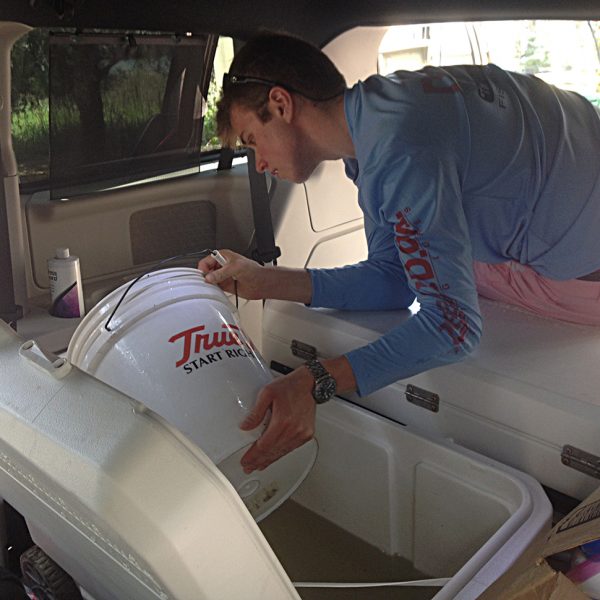
Even at hindsight, the plan still seems a little insane. But it worked. We indeed managed to catch spawning silversides at the Georgia site and then transported them immediately back to our Rankin Lab, which involved another 17 hours of driving back. After securing samples from Patchogue, we indeed managed to cross single parents from each site to produce full-sib crosses that will later be used to produce what geneticist call a linkage map. Other across and within-population crosses will be used to study gene expression at two different temperatures or raise adults for producing an F2 generation.
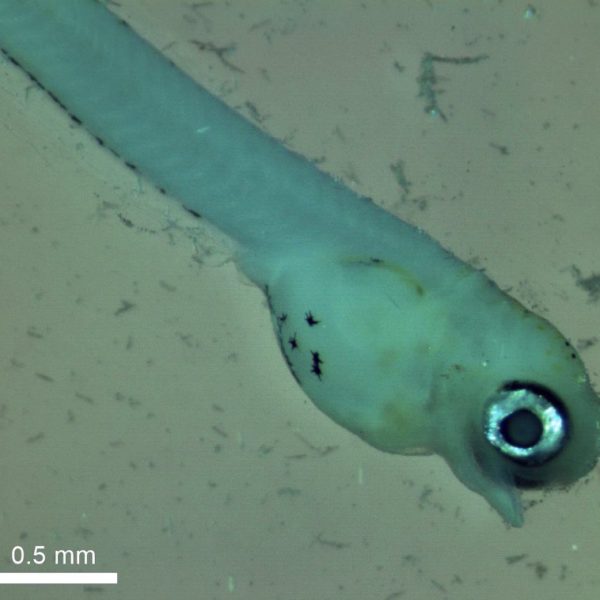
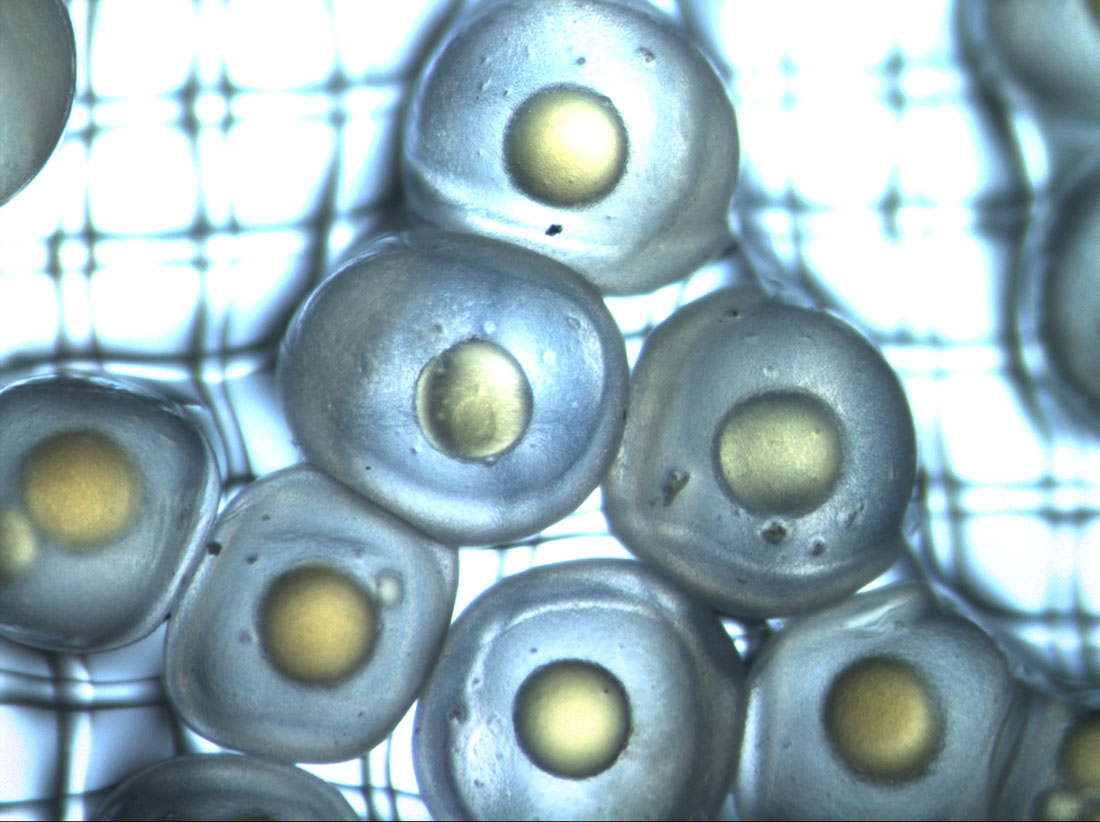
The silverside larvae are currently well, feeding, and growing up nicely. We all cross fingers for this enterprise to end in good samples and a step forward for genetic studies on a marine fish.