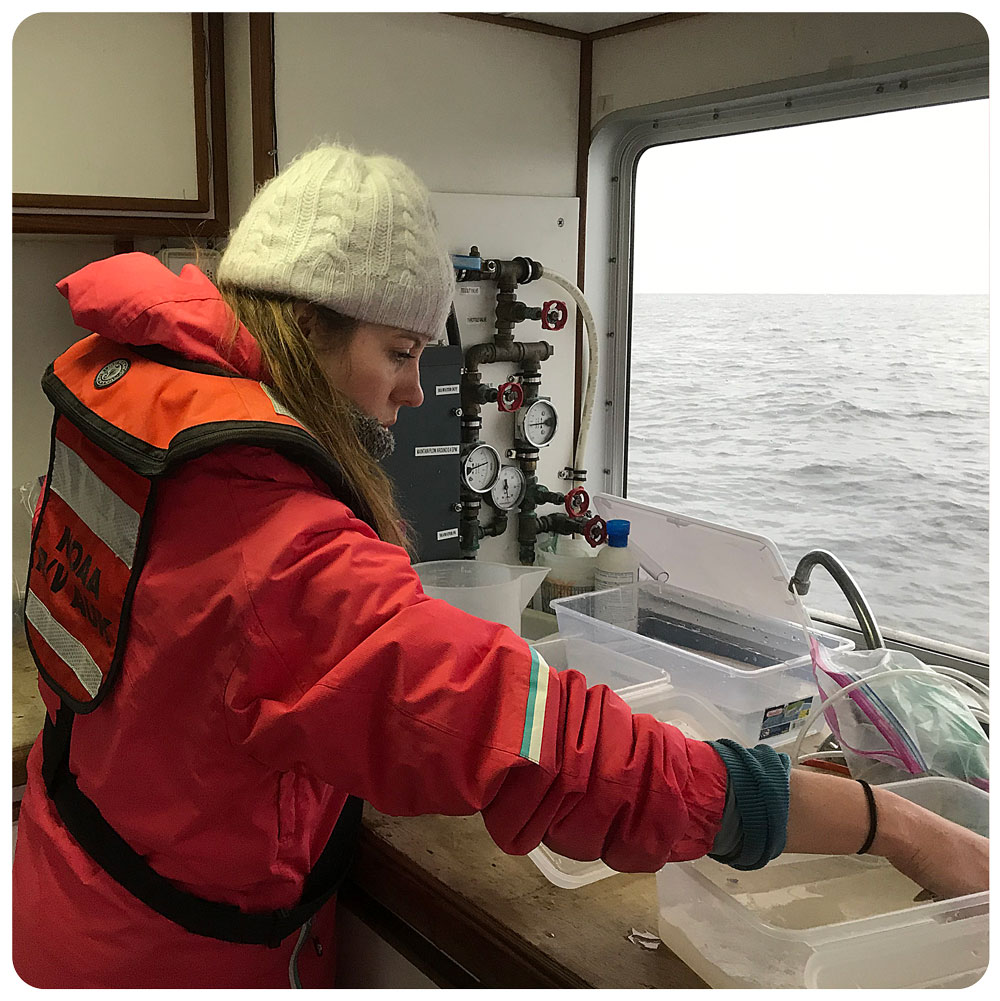
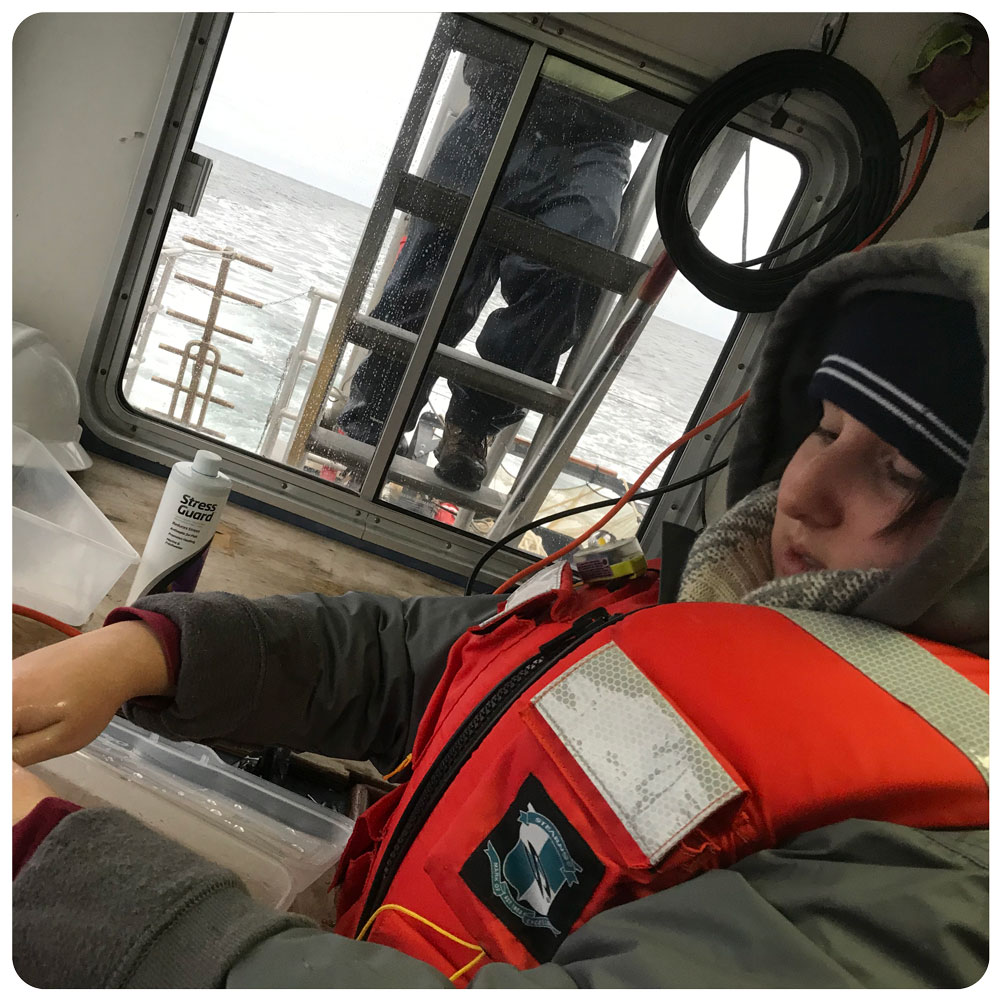
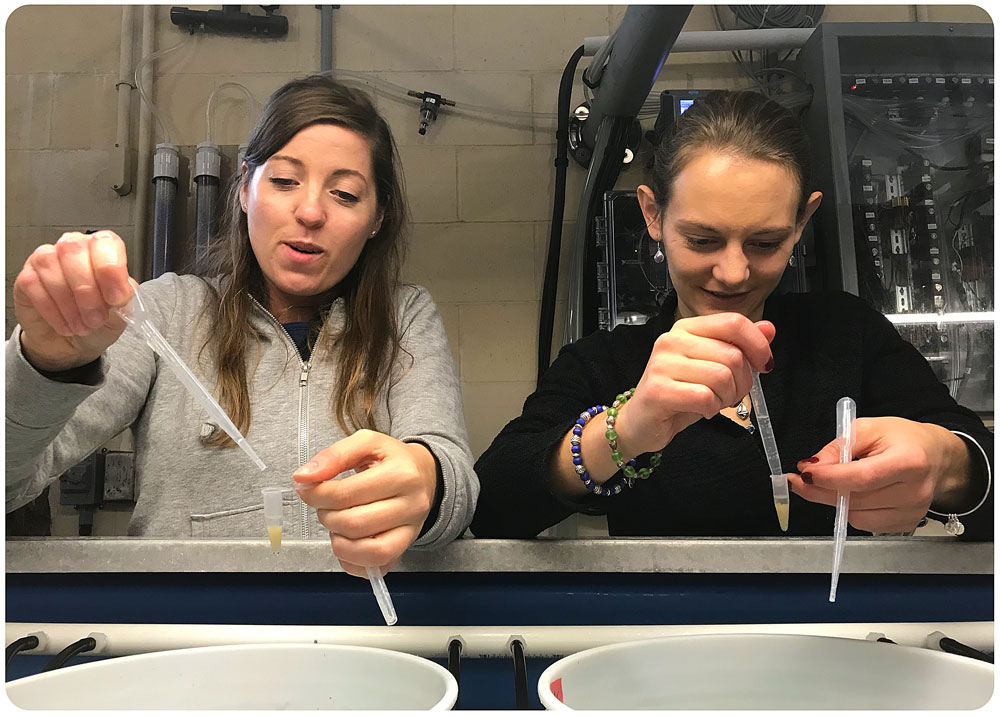
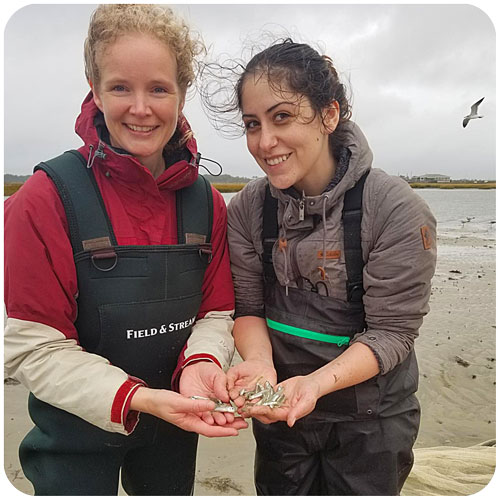
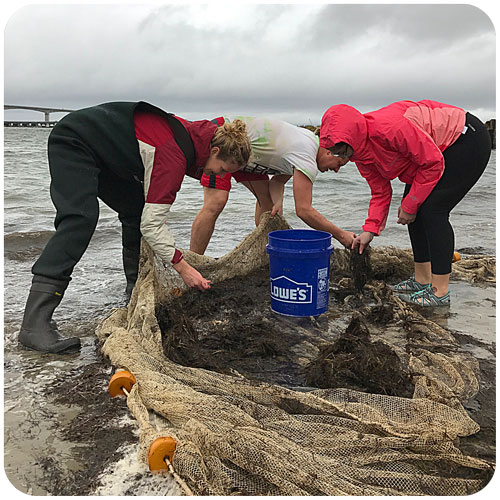
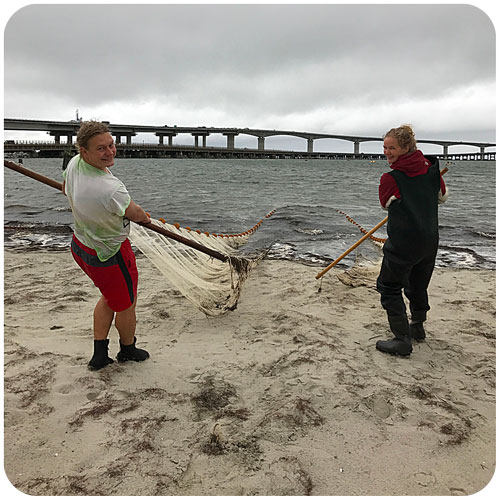
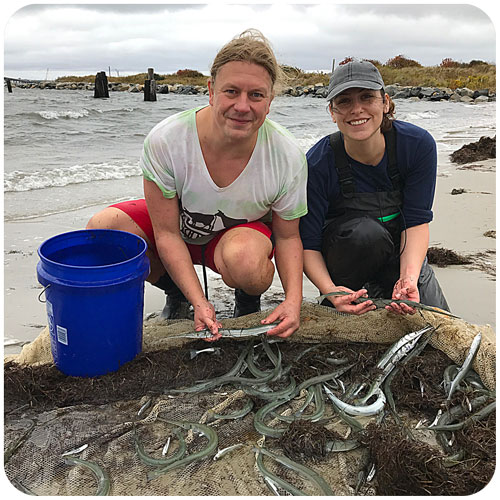
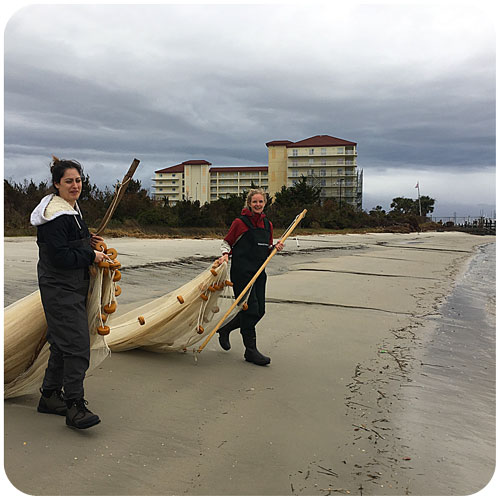
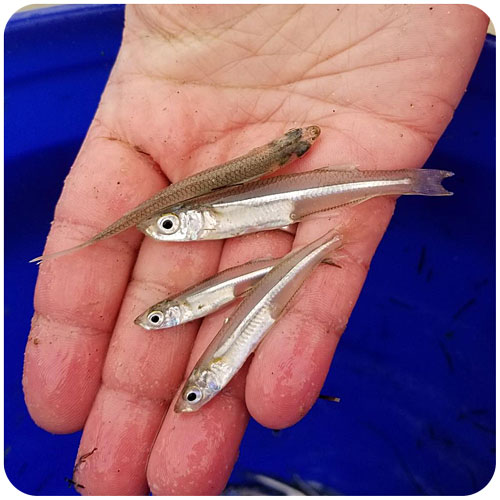
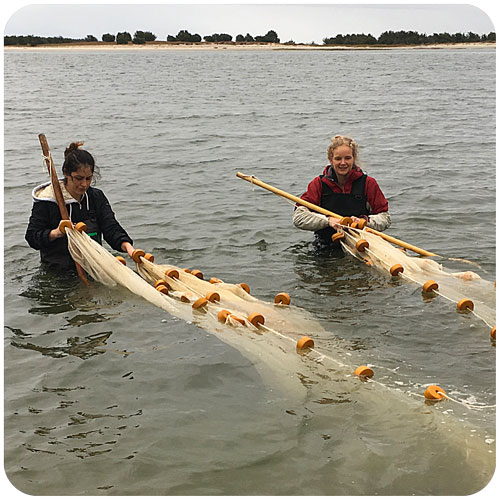
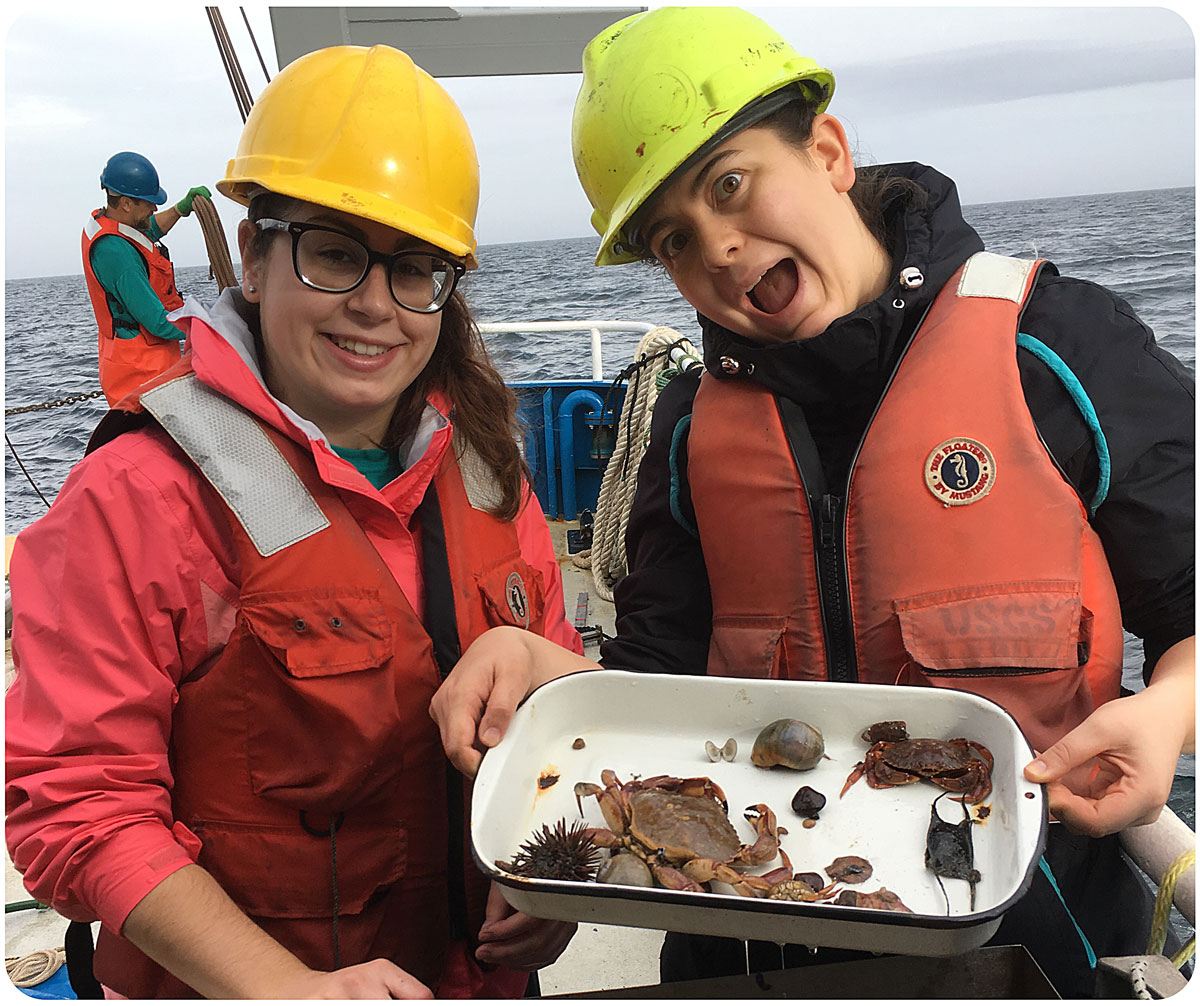
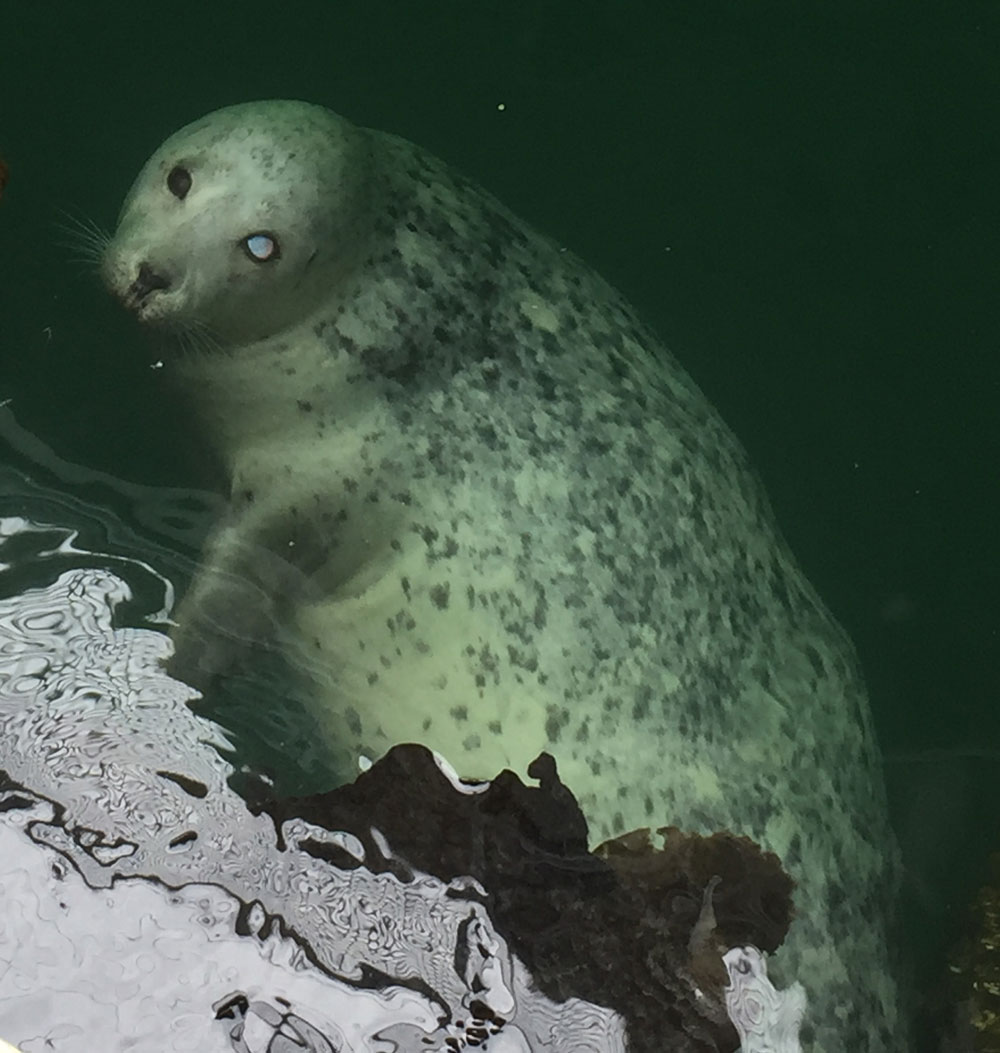
The goal of the sandlance cruise was to collect running ripe males and females to do a fertilization via strip spawning. Emma and I were a bit doubtful at first because we got less than 10 sandlance on the first two trolls. However, things got much better by the afternoon, and our most successful trawl caught 147 sand lance. I helped out with the fertilization and deploying the trawl, two things I have never done before. The most exciting part of the day was getting to see humpback whales. Usually they are in the distance but today they were right next to the boat. Everyone on board said that this never happens and it was very unusual so I felt very lucky to have seen whales at such a close proximity.”
Overall, the trip was a huge success and it was very refreshing to see everything go as planned. The only downside to the day was driving back home through a snowstorm. I later found out that there was a 73% fertilization success and we got 27,000 embryos for Emma’s experiment. I am very grateful to have gotten the opportunity to help out on this sampling cruise and am looking forward to doing this again in the future!