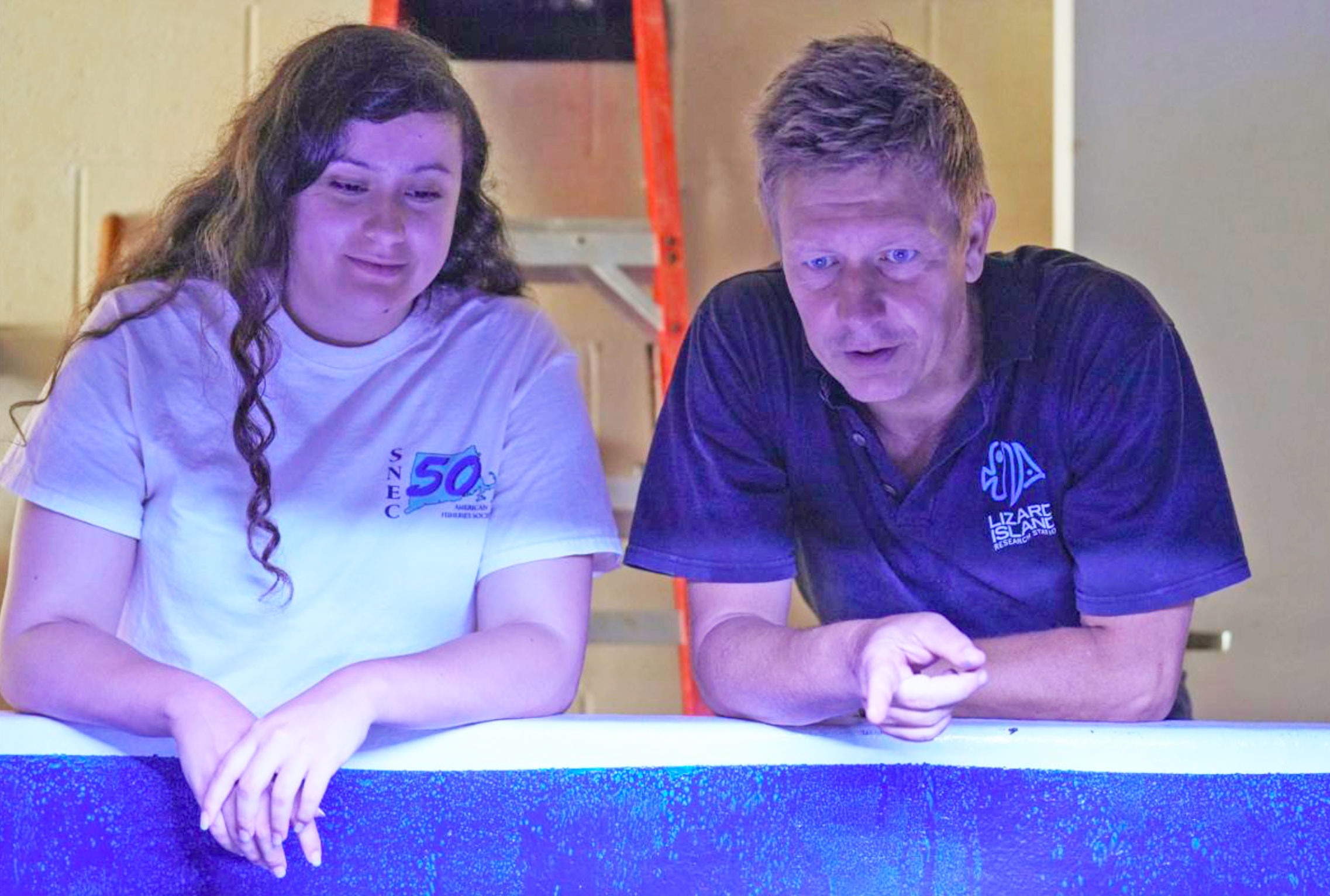
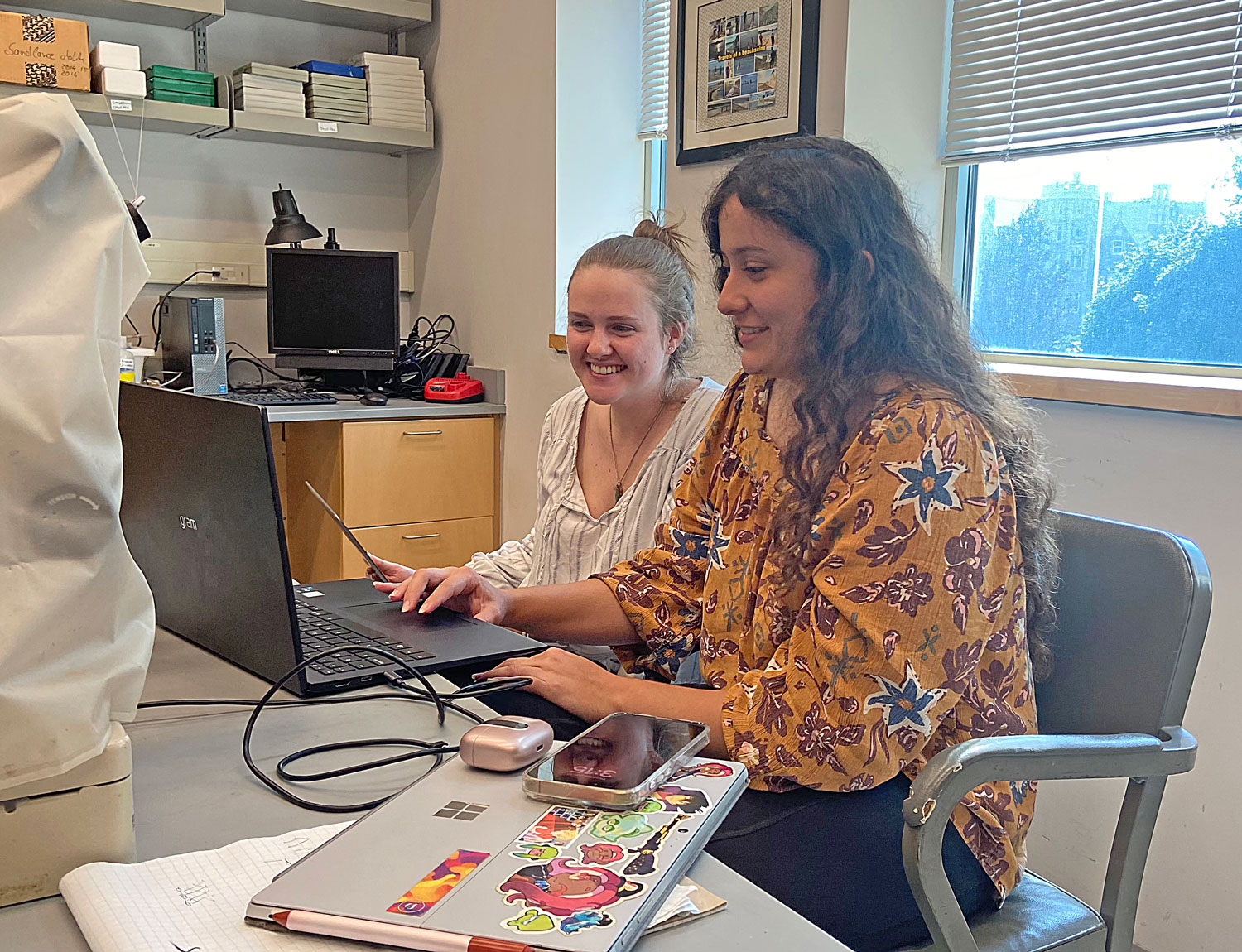
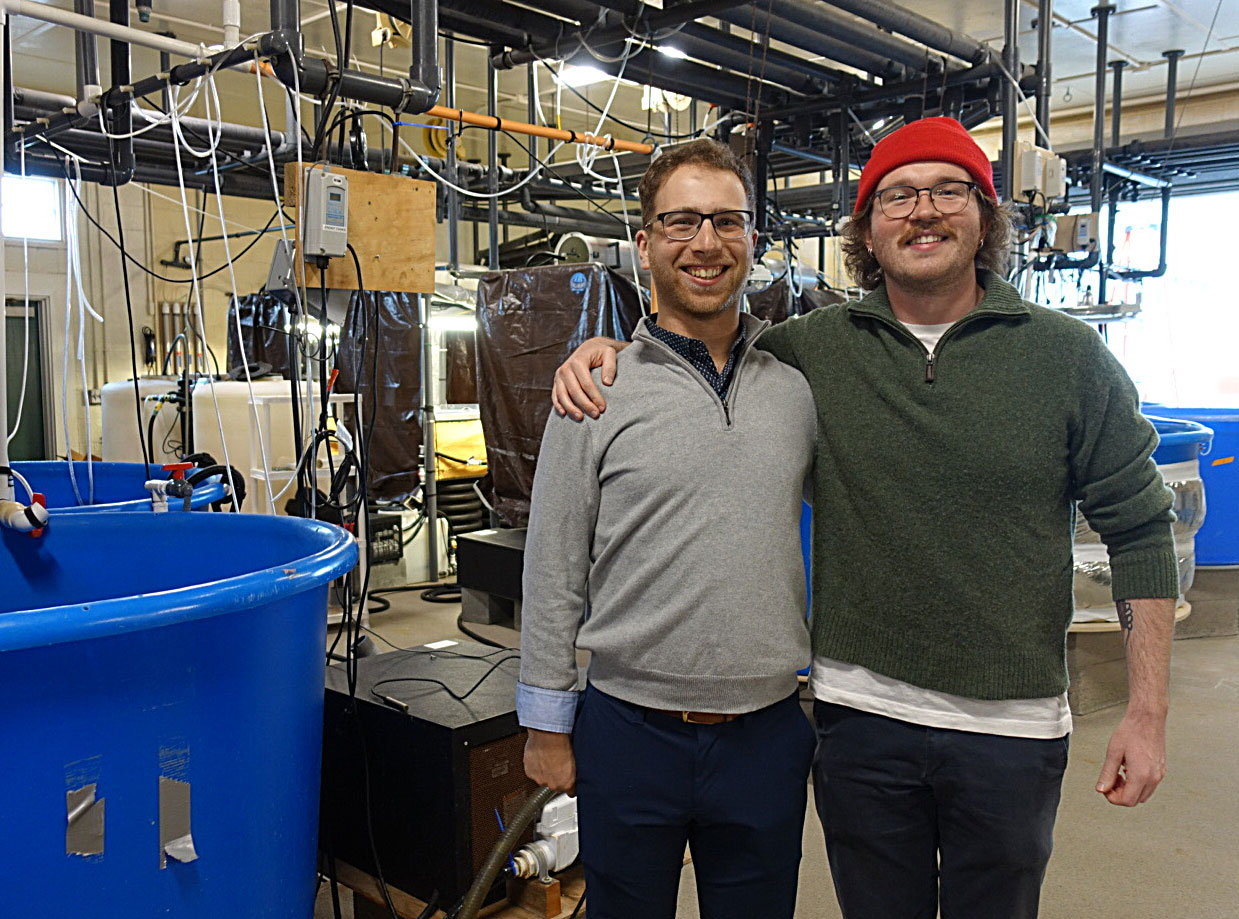
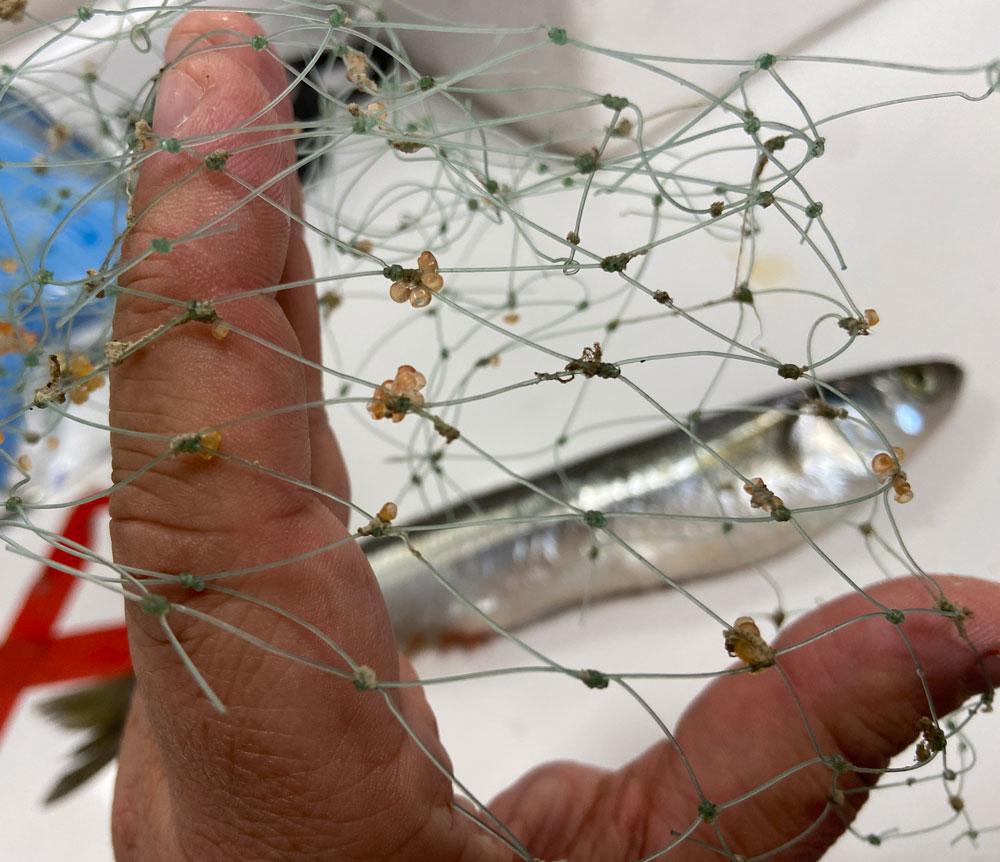
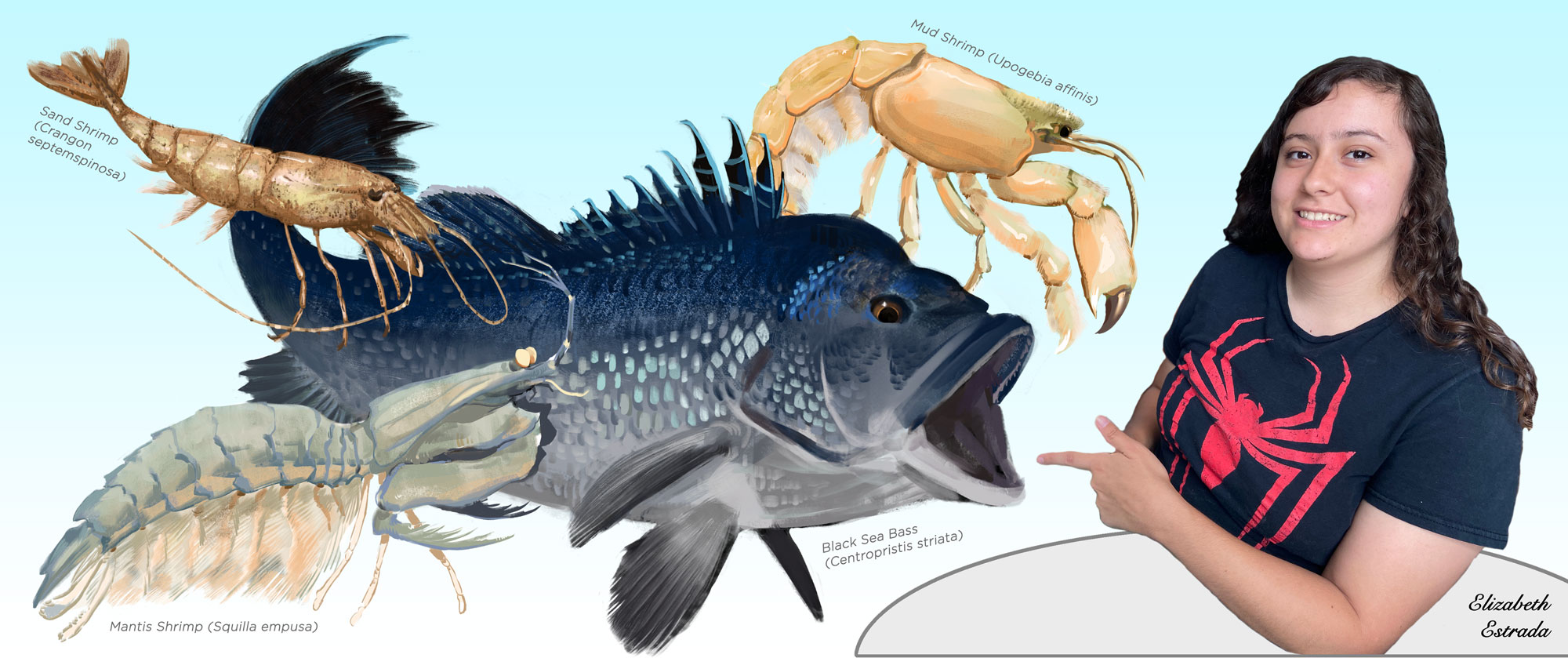
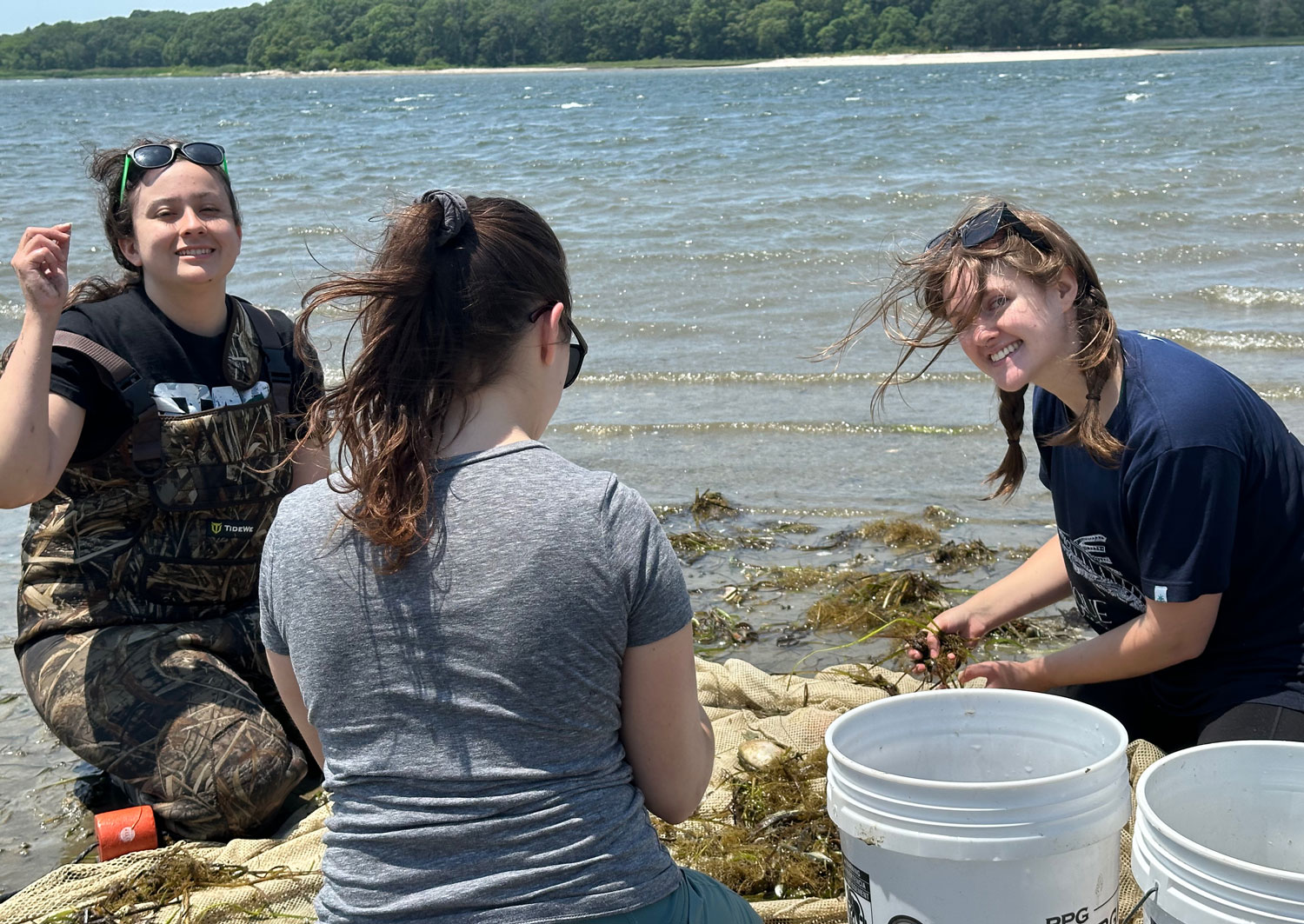8 August 2025. For 10 weeks in summer 2025, Elizabeth Estrada, a rising junior at Riverside City College in Riverside, CA, joined our lab to experience fish ecology research. She applied herself to two contemporary topics - (a) the morphometric relationships between Black sea bass predators and their crustacean prey and (b) the diurnal behavior of juvenile American sandlance in captivity. Ever curious, Elizabeth learned what motivates this research, contributed valuable data and observations, and shadowed other graduate students to observe molecular techniques.
And Elizabeth's artistic talents in drawing animals will leave a truly lasting legacy at our lab!
Thank you so much for your hard work, curiosity and inspiration, Elizabeth! The whole Baumann lab wishes you all the best for the future!
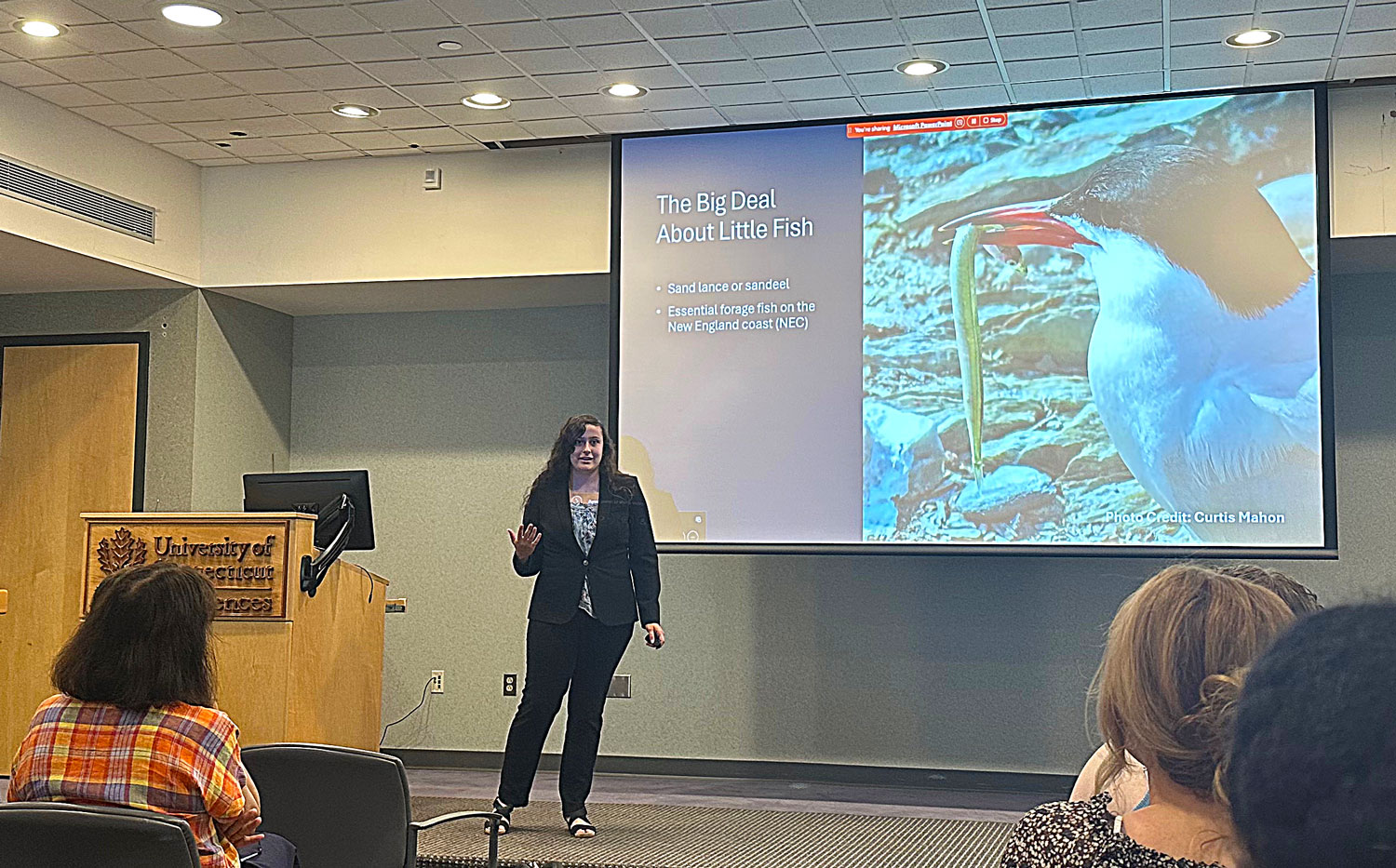
Elizabeth summarized her summer research findings during one poster and one oral presentation.
- Estrada, E., Siegfried, E., and Baumann, H. 2025. Diurnal Burying Behavior of Ammodytes spp. REU final colloquium, Avery Point 6 August 2025
- Estrada, E., Roby, H., and Baumann, H. 2025. Breaking it down: do bigger fish eat bigger shrimp? REU outreach event to the broader public at Mystic Aquarium. 22 July 2025
You can reach Elizabeth at eestrada75@student.rccd.edu