This research feature makes the case for multistressor research to a broad general audience and introduces our NSF project and its participants. Download the feature by clicking on the pictures or the link below.
People
[Research news] Are sand lance embryos particularly sensitive to high CO2?
On this dimly lit November afternoon, rain mercilessly drenched scientists and crew on board the R/V Auk as it slowly navigated the waters of Stellwagen Bank. A world like a wet sponge. Sky and ocean, indistinguishable.
Thanksgiving, the next day.
Despite the circumstances, the team’s mood was nothing short of elated. Our small beam trawl had just spilled hundreds of silvery fish on deck, wriggling like eels. They were Northern sand lance (Ammodytes dubius).
Running ripe adults.
Spawning.
Apparently, they like Thanksgiving, too.
—————
As the ship docked back in the Scituate, Mass., harbor that day, the rain thinned to hazy darkness.
“Let’s get a coffee and then on the road,” mumbled Chris, who led the team, “the real work of the experiments has just begun.”
Sand lance have a few interesting and rare characteristics. They alternate between schooling and foraging in the upper water column and extended periods of being almost completely buried in sand. For that, they rely on sand of a particular grain size and with very little organic content. It’s the kind of sand that defines large areas of the Stellwagen Bank.
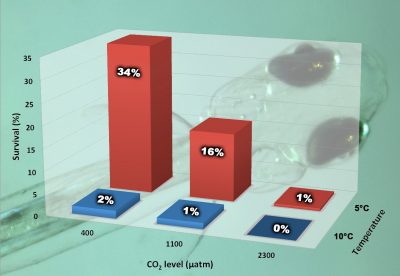
Surprisingly little is known about the ecology and ecosystem importance of this sand lance species, although research on its European relatives (A. tobianus, A. marinus) is more advanced. In particular, experiments on early life stages of Northern sand lance have been lacking, save for some pioneering work on rearing methods of the related A. americanus (Smigielski et al. 1984). One question that was of particular interest to our lab involved the potential sensitivity of this fish species to carbon dioxide (CO2). That’s due to two other interesting and rare characteristics of sand lance. They spawn in late fall and winter in cold (and still cooling) waters, which is why their eggs and larvae develop extremely slow compared to other, more typical spring and summer spawning species. In addition, the species is found not in nearshore, but offshore coastal waters, where smaller seasonal and daily CO2 fluctuations more closely resemble oceanic conditions. Could sand lance offspring be particularly sensitive to higher levels of oceanic carbon dioxide predicted during the next 100 to 300 years as climate change effects intensify?
Our experiments are still ongoing, and rearing protocols are being improved.
The preliminary findings, however, are stunning. Survival to hatch was dramatically reduced under elevated and high compared to baseline CO2 conditions. It was severely lowered at higher (10°C or 50°F) compared to lower temperatures (5°C or 41°F). Our second experiment this year appears to repeat this pattern. If these results continue, that would mean sand lance is one of the most CO2-sensitive species studied to date.
General interest in sand lance goes beyond its sensitivity to carbon dioxide. Given the species importance for the ecosystem and coastal economy, there are now increasing efforts to better understand sand lance feeding ecology, distribution and relationship to the rest of the food web. In this regard, funding of our project by the Northeast Sea Grant Consortium proved prescient and a seed for subsequent grants from MIT Sea Grant and the Bureau of Energy Management (BOEM) to continue the work. Surely, the groundswell of interest in sand lance is commensurate with its importance and will enable insights into better management strategies for sensitive ecosystems like those along the U.S. Atlantic coast.
Collaborators on this project are: D. Wiley of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration-Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary; P. Valentine of the U.S. Geological Survey; and S. Gallagher and J. Llopiz, both of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
[Lab news] Live, feeding sand lance larvae
17 January 2018. Since November 2017, we have ongoing experiments with offspring of Northern sand lance (Ammodytes dubius), a winter-spawning forage fish of ecological importance along the North-American Atlantic coast. The clip below shows larvae almost two months after fertilization, developing nicely in 5C water and feeding actively on live rotifers. The experiments, led by Chris Murray for his PhD research, study the CO2 sensitivity of this species in our factorial larval rearing system. To our knowledge, this is the first time that this particular species has been reared that far under experimental conditions. Have a look!

[Lab news] Jake graduates with his Master’s degree!
For his Master’s thesis, Jake painstakingly took it upon himself to retrieve and digitize the 40+ year time series of environmental observations from Project Oceanology, an ocean literacy organization that has been taking middle and high school students out to sea for decades. For the first time, his work allowed a quantitative evaluation of these data and a glimpse into the decadal changes in abiotic and biotic conditions in nearshore waters of Eastern Long Island Sound.
His Masters Thesis
“Analysis of a Newly Digitized Long-Term Dataset of Environmental Observations from Long Island Sound”
is accessible via the OpenCommons Site of the UConn Library.
During his time at the Baumann lab, Jake also conducted an experiment on potential maternal effects and their influence on offspring CO2 sensitivity, which was recently published in the Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology
- Snyder, J.T.*, Murray, C.S.*, and Baumann, H. (2018)
Potential for maternal effects on offspring CO2 sensitivities in the Atlantic silverside (Menidia menidia).
Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 499:1-8
Below is one of Jake’s timeless pictures of schooling juvenile Atlantic silversides. Many more pictures can be admired in our Imagery section or on Jake’s own Photography website RedSkiesPhotography

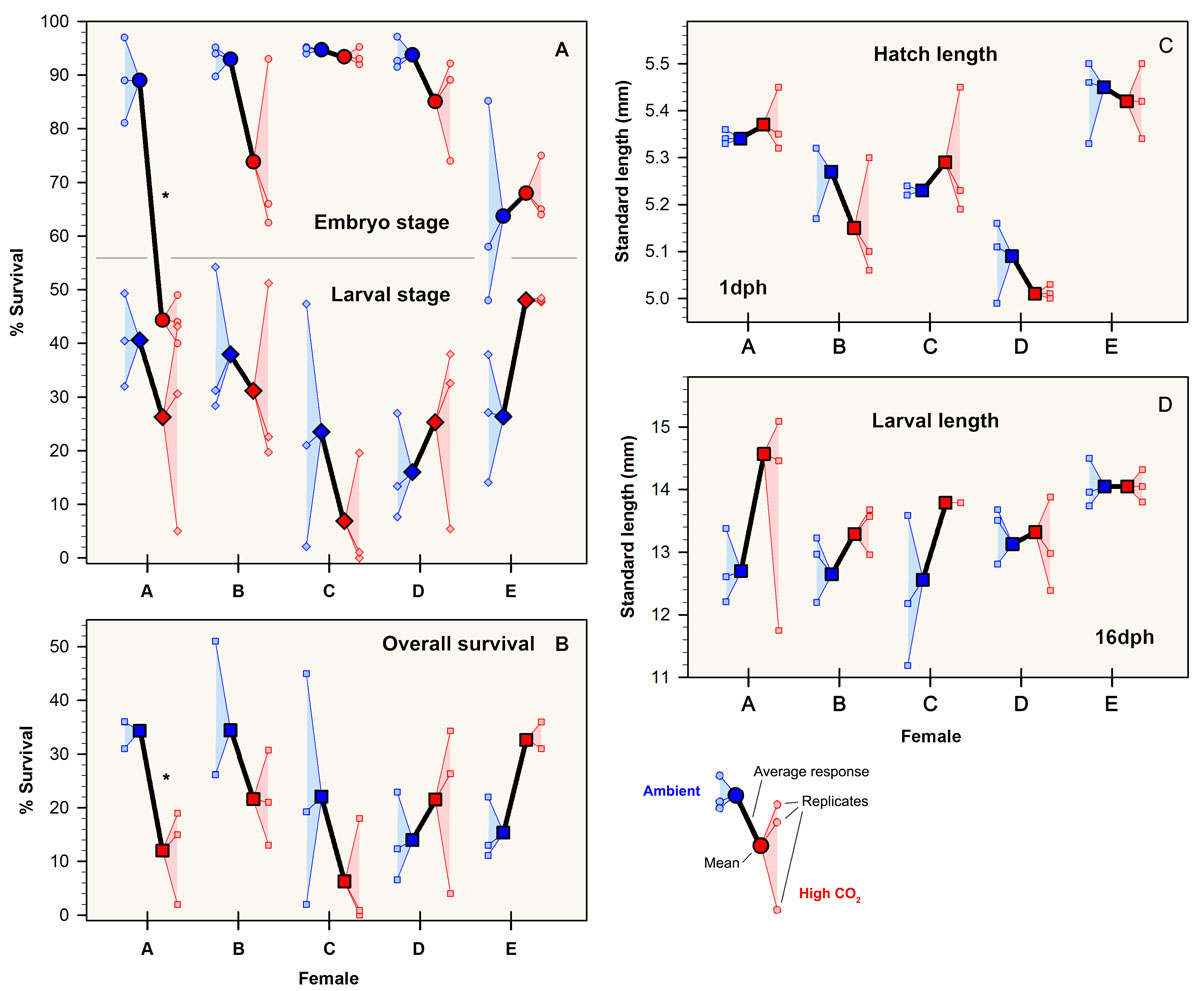
[New publication] Mothers matter for the CO2 sensitivity of fish offspring
28 November 2017. The Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology just published the latest study by our group looking at differences in the CO2 sensitivity of Atlantic silverside offspring stemming from different mothers. Congratulations to Jacob Snyder for his first peer-reviewed publication.
Among the highlights of the study:
- Offspring produced by different females varied in their sensitivity to high CO2 conditions.
- Specific fatty acids in eggs were correlated to the log-transformed CO2 response ratio of embryo survival and hatch length.
- Maternal provisioning might be an additional determinant of CO2 sensitivity in fish early life stages.
Citation:
Snyder, J.T.*, Murray, C.S.*, and Baumann, H. (2018)
Potential for maternal effects on offspring CO2 sensitivities in the Atlantic silverside (Menidia menidia).
Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 499:1-8
[Lab news] Baumann lab attends the CERF conference in Providence, RI

Together with Steve Litvin (Monterey Bay Aquarium) Hannes convened a theme session titled “Physiological ecology in the Anthropocene: linking the laboratory and field” and talked about our recently published paper on pH and oxygen fluctuations in nearshore coastal environments. Jake presented his Master thesis research on the newly digitized long-term time series of Project Oceanology, and Julie talked about the first aspect of her ongoing research on silverside otoliths and inferred patterns of growth and temperature-dependent sex determination. Well done, all!
- Baumann H. and Smith, E.M. 2017. Quantifying the covariance of pH and oxygen conditions across the diversity of US nearshore habitats.
- Pringle, J.W. and Baumann H. 2017. Sex-specific growth and mortality patterns in juvenile Atlantic silversides (Menidia menidia) from Connecticut waters.
- DeMayo, J.A., Park, G., Norton, L., Huffman, W., Finiguerra, M., Baumann H., and Dam, H.G. 2017. Combined effects of warming and acidification on life-history traits of the calanoid copepod Acartia tonsa.
- Snyder, J.T. and Baumann H. 2017. A newly digitized 45-year dataset of environmental and biological observations from Long Island Sound.
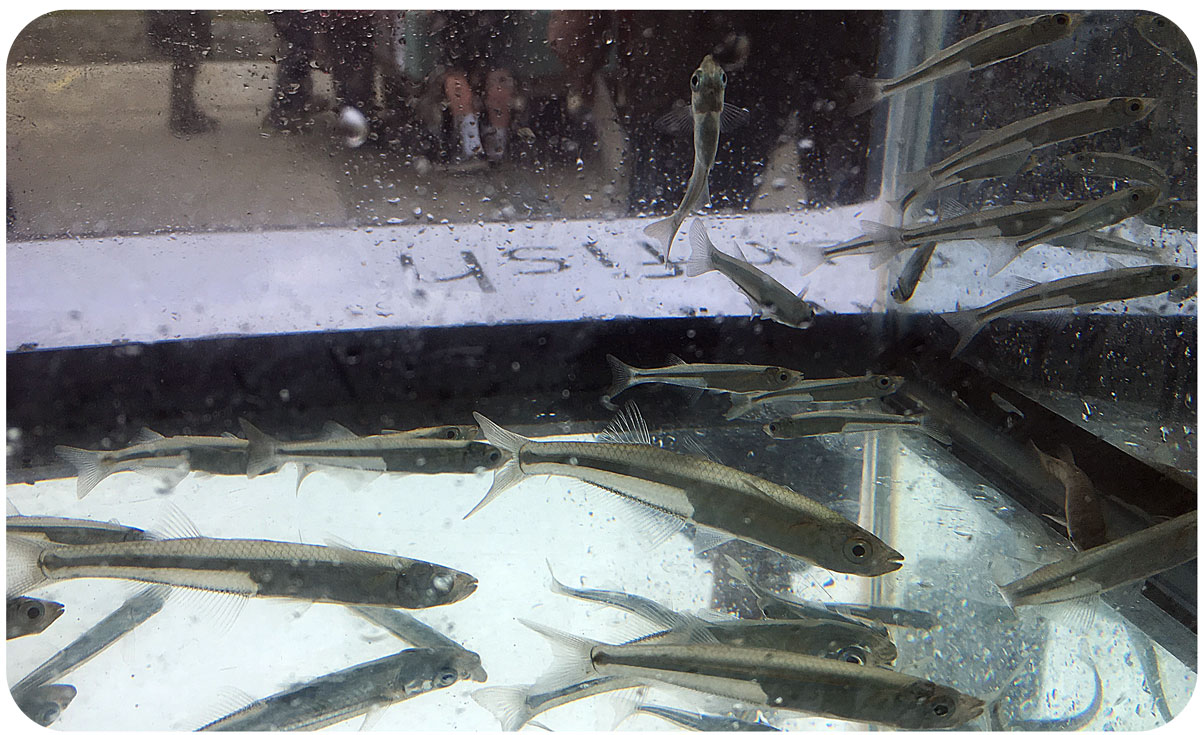
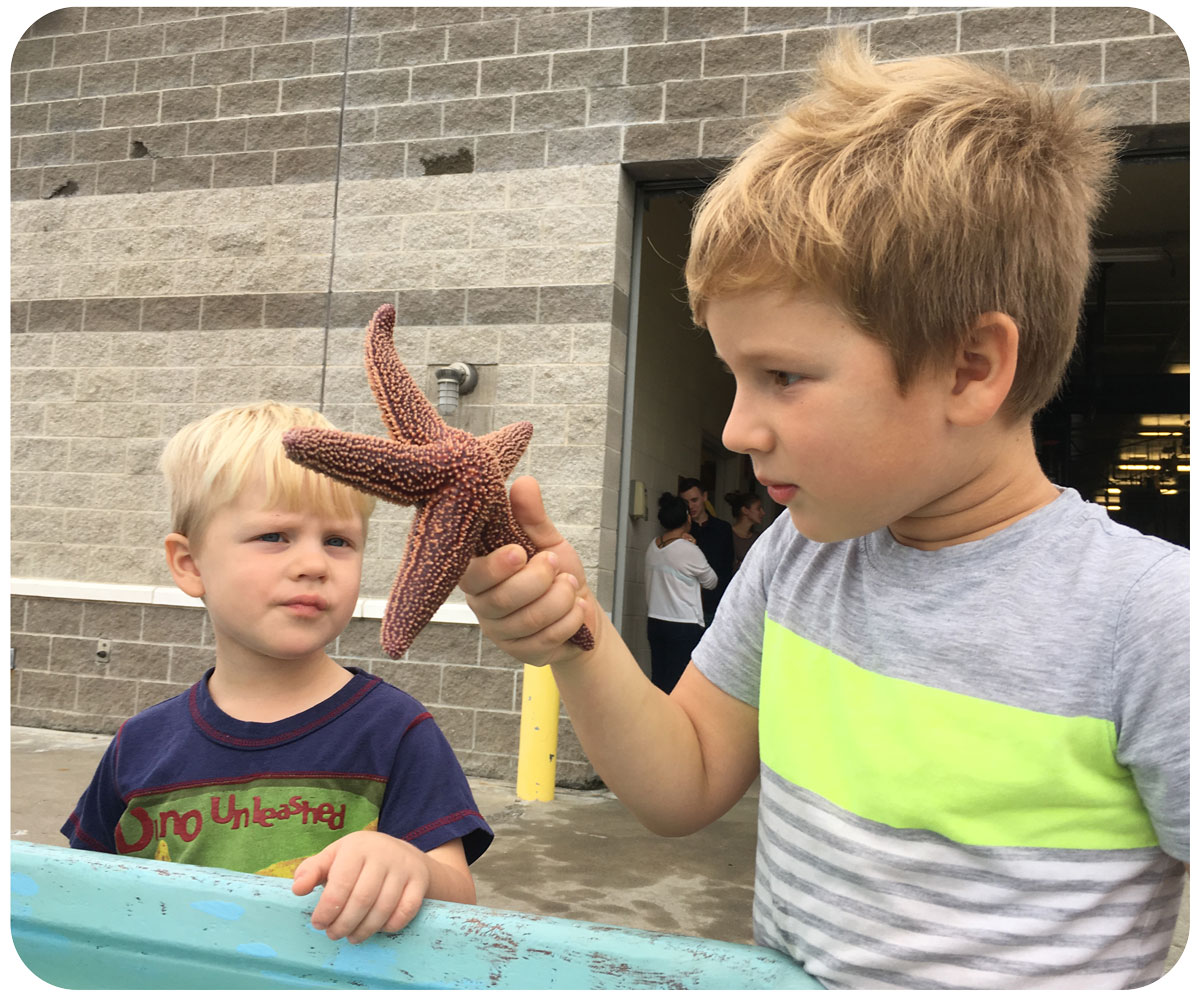
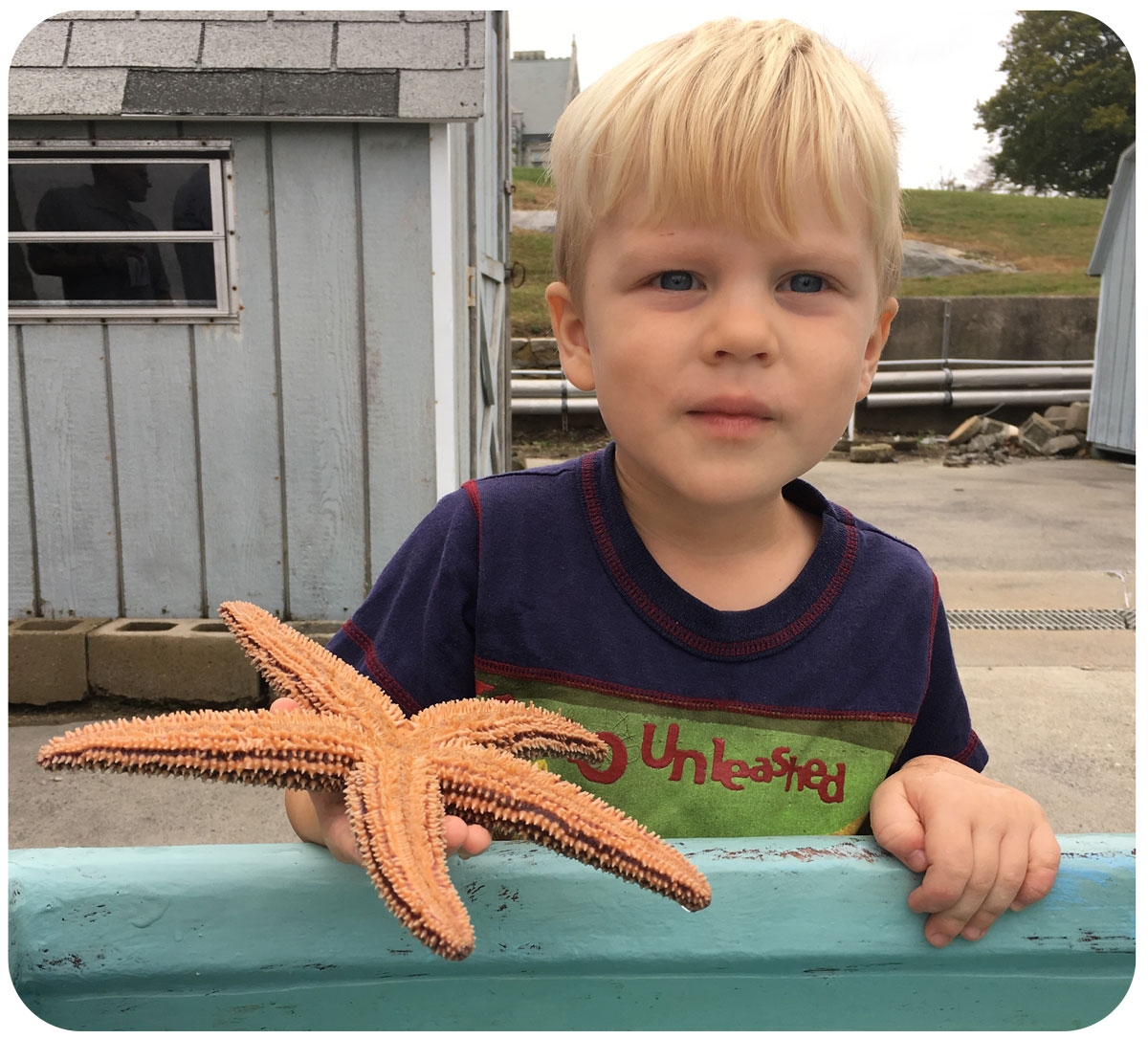
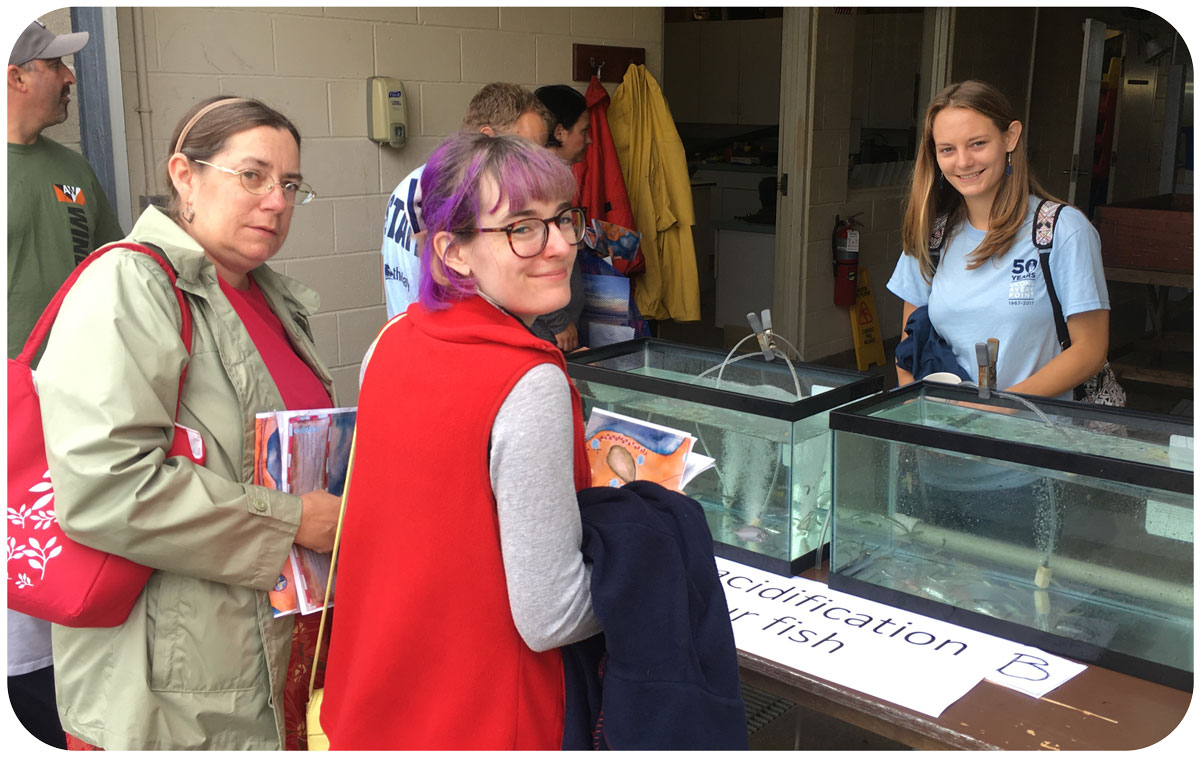
[Lab news] Baumann lab participates in Avery Point Open House Event
Our lab manned a table outside the Rankin Lab, telling people about the nearshore fish community, the phenomenon of ocean acidification and the measurement of pH in water. Everybody chipped in, thanks!
Hannes also premiered reciting Dr. Seuss’ “The Lorax” in front of young and old in the AP auditorium.
Check out some of the fun around the “Ocean Acidification and our fish” table:
[Lab news] Measuring juvenile silversides. Live.
10 October 2017. Today, Chris, Emma, and Julie measured over 400 juvenile Atlantic silversides for their length and weight. This time, however, we did not euthanize the fish before, but successfully measured them while still alive, only a little drowsy from the mild anesthetic we administered before.
Click on the video below to have a look for yourself.
Congratulations all, for a job well done!
[Lab news] Chris and Hannes attend ICES Annual Science conference
On 19-21 September 2017, Chris Murray and Hannes Baumann traveled to Fort Lauderdale, Florida, to attend the ICES (International Council for the Exploration of the Sea) Annual Science Conference in order to present our ongoing NSF and NOAA funded research on potential ocean acidification effects in Atlantic Silversides and Northern Sand lance. Due to Hurricane Irma, which had impacted all of Florida just a week earlier, it was a great relief that the conference could actually be successfully held.
Together with Chris Chambers (NOAA), Ian Bradbury (DFO, Canada), and Richard McBride (NOAA), Hannes convened a theme session titled “Patterns, sources, and consequences of intraspecific variation in responses of marine fauna to environmental stressors“.
Chris gave a talk and a poster during this session, which was well received and thus a worthwhile exposure for Chris and our lab’s research.
- Murray, C. S. and Baumann H. 2017. Growth costs of high CO2 environments in a marine fish: importance of feeding methodology. Talk.
- Murray, C. S., Wiley, D., and Baumann H. 2017. A preliminary study testing the effects of high CO2 on the early life stages of the northern sand lance Ammodytes dubius. Poster.
[Lab news] Emma Cross joins the team!
Have a look at Emma’s recent publications
“Everything is going swimmingly well so far (pun intended!). It is really great to be a part of the Baumann lab and I’m really enjoying expanding my knowledge of biological impacts of environmental change. My previous ocean acidification and warming research focussed on the effects on polar and temperate brachiopod shells so I’m now looking forward to investigating more climate change stressors and impacts on different taxa. I have already participated in my first beach seining trip exploring the local biodiversity and getting a feel for the regular fieldwork undertaken by the Baumann lab. It was lots of fun and I’m so excited to be carrying out research at an Institute located right on the ocean again! I am also enjoying living in a new country and looking forward to exploring more once I’ve finished building all my flatpack furniture!”


















